Expression of Wnt-5a and β-catenin in primary hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25031739
- PMCID: PMC4097247
Expression of Wnt-5a and β-catenin in primary hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
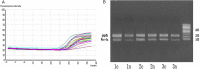
It has been reported that changes in Wnt5a expression are closely related to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development, while decreased or abnormal β-catenin expression may promote the invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. In this study, the roles and clinical significance of Wnt-5a and β-catenin expression were analyzed in primary HCC. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) analysis of Wnt-5a mRNA expression was performed in 26 fresh HCC samples and the corresponding para-carcinoma tissues. Wnt-5a and β-catenin protein expression was detected by immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded tissues of 85 cases of HCC and corresponding para-carcinoma tissues and 15 cases of hepatic cirrhosis. Results showed that Wnt-5a mRNA levels were significantly higher in HCC tissue than in the para-carcinoma tissue (0.102 ± 0.159 and 0.020 ± 0.022, respectively; P < 0.05), while Wnt-5a protein was absent or low in HCC. Wnt-5a expression was detected in significantly fewer HCC tissue samples than in the para-carcinoma and hepatic cirrhosis tissue samples (21.2% (18/85), 81.26% (69/85) and 86.7% (13/15), respectively; P < 0.01). Abnormal localization of β-catenin protein shown by intracytoplasmic or intranuclear staining was observed in 72.94% (62/85) of HCC samples. These observations indicate that the role of Wnt-5a in HCC is mediated at the protein level rather than the transcriptional level. Furthermore, the abnormal localization of β-catenin observed in HCC tissues may be associated with gene mutation leading to the generation of truncated β-catenin proteins, which in turn, may represent an initiating or contributing factor in the development of HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; RT-PCR; Wnt-5a; immunohistochemistry; β-catenin.
Figures


References
-
- Ding J, Huang S, Wu S, Zhao Y, Liang L, Yan M, Ge C, Yao J, Chen T, Wan D, Wang H, Gu J, Yao M, Li J, Tu H, He X. Gain of miR-151 on chromosome 8q24.3 facilitates tumour cell migration and spreading through downregulating RhoGDIA. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:390–399. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R. Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Cell Res. 2008;18:523–527. - PubMed
-
- Groen RW, Oud ME, Schilder-Tol EJ, Overdijk MB, ten Berge D, Nusse R, Spaargaren M, Pals ST. Illegitimate WNT pathway activation by beta- catenin mutation or autocrine stimulation in T-cell malignancies. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6969–6977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
