The nutritional energy to clinical outcome relation revisited
- PMID: 25032513
- PMCID: PMC4059491
- DOI: 10.1186/cc13861
The nutritional energy to clinical outcome relation revisited
Abstract
In the previous issue of Critical Care, Dr Bellomo and colleagues reported an observational study of the relationship between nutritional intake and survival in the RENAL randomized controlled trial. In summary, the total energy intake in a very large and severely ill patient population was low. Higher average daily caloric energy intake was not associated with improved survival. The study illustrates the complexity of the interaction between disease and nutrition.
Figures
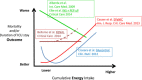
Comment on
-
Calorie intake and patient outcomes in severe acute kidney injury: findings from The Randomized Evaluation of Normal vs. Augmented Level of Replacement Therapy (RENAL) study trial.Crit Care. 2014 Mar 14;18(2):R45. doi: 10.1186/cc13767. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24629036 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bellomo R, Cass A, Cole L, Finfer S, Gallagher M, Lee J, Lo S, McArthur C, McGuiness S, Myburgh J, Norton R, Scheinkestel C. Calorie intake and patient outcomes in severe acute kidney injury: findings from The Randomized Evaluation of Normal vs. Augmented Level of Replacement Therapy (RENAL) study trial. Crit Care. 2014;18:R45. doi: 10.1186/cc13767. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellomo R, Cass A, Cole L, Finfer S, Gallagher M, Lo S, McArthur C, McGuinness S, Myburgh J, Norton R, Scheinkestel C, Su S. Intensity of continuous renal-replacement therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1627–1638. - PubMed
-
- Heidegger CP, Berger MM, Graf S, Zingg W, Darmon P, Costanza MC, Thibault R, Pichard C. Optimisation of energy provision with supplemental parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet. 2013;381:385–393. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61351-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Doig GS, Simpson F, Sweetman EA, Finfer SR, Cooper DJ, Heighes PT, Davies AR, O'Leary M, Solano T, Peake S. Early parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients with short-term relative contraindications to early enteral nutrition: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2013;309:2130–2138. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.5124. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

