Glial development: the crossroads of regeneration and repair in the CNS
- PMID: 25033178
- PMCID: PMC4114724
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.06.010
Glial development: the crossroads of regeneration and repair in the CNS
Abstract
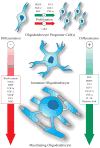
Given the complexities of the mammalian CNS, its regeneration is viewed as the holy grail of regenerative medicine. Extraordinary efforts have been made to understand developmental neurogenesis, with the hopes of clinically applying this knowledge. CNS regeneration also involves glia, which comprises at least 50% of the cellular constituency of the brain and is involved in all forms of injury and disease response, recovery, and regeneration. Recent developmental studies have given us unprecedented insight into the processes that regulate the generation of CNS glia. Because restorative processes often parallel those found in development, we will peer through the lens of developmental gliogenesis to gain a clearer understanding of the processes that underlie glial regeneration under pathological conditions. Specifically, this review will focus on key signaling pathways that regulate astrocyte and oligodendrocyte development and describe how these mechanisms are reutilized in these populations during regeneration and repair after CNS injury.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aguirre A, Dupree JL, Mangin JM, Gallo V. A functional role for EGFR signaling in myelination and remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:990–1002. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht PJ, Murtie JC, Ness JK, Redwine JM, Enterline JR, Armstrong RC, Levison SW. Astrocytes produce CNTF during the remyelination phase of viral-induced spinal cord demyelination to stimulate FGF-2 production. Neurobiol Dis. 2003;13:89–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01NS045702/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS071153/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS062686/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD040677/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS056427/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS071153/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD024064/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30HD40677/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30HD024064/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS056427/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS062686/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045702/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

