Amphetamine modulates excitatory neurotransmission through endocytosis of the glutamate transporter EAAT3 in dopamine neurons
- PMID: 25033183
- PMCID: PMC4159050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.043
Amphetamine modulates excitatory neurotransmission through endocytosis of the glutamate transporter EAAT3 in dopamine neurons
Abstract
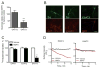
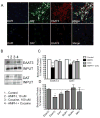
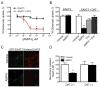
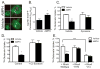
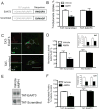
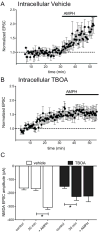
Amphetamines modify the brain and alter behavior through mechanisms generally attributed to their ability to regulate extracellular dopamine concentrations. However, the actions of amphetamine are also linked to adaptations in glutamatergic signaling. We report here that when amphetamine enters dopamine neurons through the dopamine transporter, it stimulates endocytosis of an excitatory amino acid transporter, EAAT3, in dopamine neurons. Consistent with this decrease in surface EAAT3, amphetamine potentiates excitatory synaptic responses in dopamine neurons. We also show that the process of internalization is dynamin- and Rho-mediated and requires a unique sequence in the cytosolic C terminus of EAAT3. Introduction of a peptide based on this motif into dopamine neurons blocks the effects of amphetamine on EAAT3 internalization and its action on excitatory responses. These data indicate that the internalization of EAAT3 triggered by amphetamine increases glutamatergic signaling and thus contributes to the effects of amphetamine on neurotransmission.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adie EJ, Francis MJ, Davies J, Smith L, Marenghi A, Hather C, Hadingham K, Michael NP, Milligan G, Game S. CypHer 5: a generic approach for measuring the activation and trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors in live cells. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2003;1:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Aked J, Coizet V, Clark D, Overton PG. Local injection of a glutamate uptake inhibitor into the ventral tegmental area produces sensitization to the behavioural effects of d-amphetamine. Neuroscience. 2005;134:361–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

