Enhancement of electroporation facilitated immunogene therapy via T-reg depletion
- PMID: 25034887
- PMCID: PMC4139741
- DOI: 10.1038/cgt.2014.35
Enhancement of electroporation facilitated immunogene therapy via T-reg depletion
Abstract
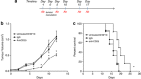
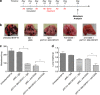
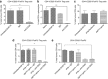
Regulatory T cells (T-regs) can negatively impact tumor antigen-specific immune responses after infiltration into tumor tissue. However, depletion of T-regs can facilitate enhanced anti-tumor responses, thus augmenting the potential for immunotherapies. Here we focus on treating a highly aggressive form of cancer using a murine melanoma model with a poor prognosis. We utilize a combination of T-reg depletion and immunotherapy plasmid DNA delivered into the B16F10 melanoma tumor model via electroporation. Plasmids encoding murine granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human B71 were transfected with electroporation into the tumor and transient elimination of T-regs was achieved with CD25-depleting antibodies (PC61). The combinational treatment effectively depleted T-regs compared to the untreated tumor and significantly reduced lung metastases. The combination treatment was not effective in increasing the survival, but only effective in suppression of metastases. These results indicate the potential for combining T-reg depletion with immunotherapy-based gene electrotransfer to decrease systemic metastasis and potentially enhance survival.
Figures


References
-
- Erdmann F, Lortet-Tieulent J, Schu J, Zeeb H, Greinert R, Breitbart EW, et al. International trends in the incidence of malignant melanoma 1953–2008—are recent generations at higher or lower risk. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:385–400. - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AMM. Advances in systemic treatment of melanoma. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Dummer R, Hauschild A, Guggenheim M, Jost L, Pentheroudakis G. Melanoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2010;5:194–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

