Protective effects of Andrographis paniculata extract and pure andrographolide against chronic stress-triggered pathologies in rats
- PMID: 25035059
- PMCID: PMC11488858
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-014-0086-1
Protective effects of Andrographis paniculata extract and pure andrographolide against chronic stress-triggered pathologies in rats
Abstract
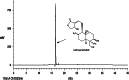
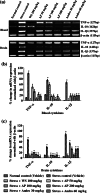
This study was designed to experimentally verify the possibility that Andrographis paniculata could be another medicinal herb potentially useful for prevention of diverse spectrums of pathologies commonly associated with chronic unavoidable environmental stress, and whether andrographolide could as well be its quantitatively major bioactive secondary metabolite. Preventive effects of 21 daily oral 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg doses of a therapeutically used extract of the plant (AP) and 30 and 60 mg/kg/day of pure andrographolide were compared in rats subjected to 1-h daily unavoidable foot-shocks. A pharmaceutically well-standardized Withania somnifera (WS) root extract was used as a reference herbal anti-stress agent in all experiments. Effects of the treatments on stress-induced alterations in body weight, gastric ulcer, adrenal and spleen weights, and depressive state and sexual behavior in male rats were quantified. Other parameters quantified were plasma cortisol levels, and expressions of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-10 and IL-1β in blood and brain. All observed stress-induced pathological changes were less pronounced or completely prevented by both AP and pure andrographolide. Even the lowest tested doses of AP (50 mg/kg/day) or of andrographolide (30 mg/kg/day) suppressed almost maximally the blood IL-1β and IL-10 as well as brain TNF-α and IL-10 expressions induced by chronic stress. Qualitatively, the observed activity profiles of both of them were similar to those of WS dose tested. These results reveal that both AP and andrographolide are pharmacologically polyvalent anti-stress agents, and that biological processes regulating corticosterone and cytokine homeostasis are involved in their modes of actions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Bhargava KP, Singh N (1981) Anti-stress activity of Ocimum sanctum Linn. Indian J Med Res 73:443–451 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya SK, Muruganandam AV (2003) Adaptogenic activity of Withania somnifera: an experimental study using a rat model of chronic stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:547–555 - PubMed
-
- Boonstra R (2013) Reality as the leading cause of stress: rethinking the impact of chronic stress in nature. Funct Ecol 27:11–23
-
- Chandrasekaran CV, Thiyagarajan P, Sundarajan K, Goudar KS, Deepak M, Murali B, Allan JJ, Agarwal A (2009) Evaluation of the genotoxic potential and acute oral toxicity of standardized extract of Andrographis paniculata (KalmCold™). Food Chem Toxicol 47:1892–1902 - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekaran CV, Gupta A, Agarwal A (2010) Effect of an extract of Andrographis paniculata leaves on inflammatory and allergic mediators in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol 129:203–207 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

