Lhx1 maintains synchrony among circadian oscillator neurons of the SCN
- PMID: 25035422
- PMCID: PMC4137275
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03357
Lhx1 maintains synchrony among circadian oscillator neurons of the SCN
Abstract
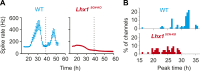
The robustness and limited plasticity of the master circadian clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is attributed to strong intercellular communication among its constituent neurons. However, factors that specify this characteristic feature of the SCN are unknown. Here, we identified Lhx1 as a regulator of SCN coupling. A phase-shifting light pulse causes acute reduction in Lhx1 expression and of its target genes that participate in SCN coupling. Mice lacking Lhx1 in the SCN have intact circadian oscillators, but reduced levels of coupling factors. Consequently, the mice rapidly phase shift under a jet lag paradigm and their behavior rhythms gradually deteriorate under constant condition. Ex vivo recordings of the SCN from these mice showed rapid desynchronization of unit oscillators. Therefore, by regulating expression of genes mediating intercellular communication, Lhx1 imparts synchrony among SCN neurons and ensures consolidated rhythms of activity and rest that is resistant to photic noise.
Keywords: Lhx1; Ror-alpha; VIP; circadian rhythm; suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Copyright © 2014, Hatori et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
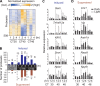
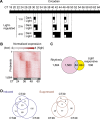
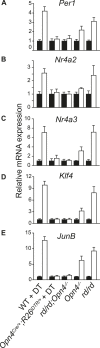


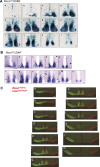




Comment in
-
The making of the master clock.Elife. 2014 Aug 20;3:e04014. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04014. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25141376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An S, Harang R, Meeker K, Granados-Fuentes D, Tsai CA, Mazuski C, Kim J, Doyle FJ, III, Petzold LR, Herzog ED. 2013. A neuropeptide speeds circadian entrainment by reducing intercellular synchrony. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 110:E4355–E4361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307088110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

