Origin and functions of tissue macrophages
- PMID: 25035951
- PMCID: PMC4470379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.013
Origin and functions of tissue macrophages
Abstract
Macrophages are distributed in tissues throughout the body and contribute to both homeostasis and disease. Recently, it has become evident that most adult tissue macrophages originate during embryonic development and not from circulating monocytes. Each tissue has its own composition of embryonically derived and adult-derived macrophages, but it is unclear whether macrophages of distinct origins are functionally interchangeable or have unique roles at steady state. This new understanding also prompts reconsideration of the function of circulating monocytes. Classical Ly6c(hi) monocytes patrol the extravascular space in resting organs, and Ly6c(lo) nonclassical monocytes patrol the vasculature. Inflammation triggers monocytes to differentiate into macrophages, but whether resident and newly recruited macrophages possess similar functions during inflammation is unclear. Here, we define the tools used for identifying the complex origin of tissue macrophages and discuss the relative contributions of tissue niche versus ontological origin to the regulation of macrophage functions during steady state and inflammation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
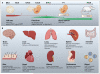

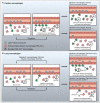
References
-
- Ajami B, Bennett JL, Krieger C, Tetzlaff W, Rossi FM. Local self-renewal can sustain CNS microglia maintenance and function throughout adult life. Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:1538–1543. - PubMed
-
- Ajami B, Bennett JL, Krieger C, McNagny KM, Rossi FM. Infiltrating monocytes trigger EAE progression, but do not contribute to the resident microglia pool. Nat. Neurosci. 2011;14:1142–1149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

