Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy
- PMID: 25035953
- PMCID: PMC4137410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010
Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy
Erratum in
- Immunity. 2014 Nov 20;41(5):866
Abstract
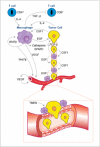
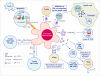
The tumor microenvironment is a complex ecology of cells that evolves with and provides support to tumor cells during the transition to malignancy. Among the innate and adaptive immune cells recruited to the tumor site, macrophages are particularly abundant and are present at all stages of tumor progression. Clinical studies and experimental mouse models indicate that these macrophages generally play a protumoral role. In the primary tumor, macrophages can stimulate angiogenesis and enhance tumor cell invasion, motility, and intravasation. During monocytes and/or metastasis, macrophages prime the premetastatic site and promote tumor cell extravasation, survival, and persistent growth. Macrophages are also immunosuppressive, preventing tumor cell attack by natural killer and T cells during tumor progression and after recovery from chemo- or immunotherapy. Therapeutic success in targeting these protumoral roles in preclinical models and in early clinical trials suggests that macrophages are attractive targets as part of combination therapy in cancer treatment.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer cell. 2005;7:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill FR, Mantovani A. Cancer-related inflammation: common themes and therapeutic opportunities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012;22:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Belai EB, de Oliveira CE, Gasparoto TH, Ramos RN, Torres SA, Garlet GP, Cavassani KA, Silva JS, Campanelli AP. PD-1 blockage delays murine squamous cell carcinoma development. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:424–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

