A certified plasmid reference material for the standardisation of BCR-ABL1 mRNA quantification by real-time quantitative PCR
- PMID: 25036192
- PMCID: PMC4320294
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2014.217
A certified plasmid reference material for the standardisation of BCR-ABL1 mRNA quantification by real-time quantitative PCR
Abstract
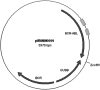
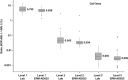
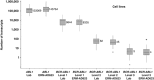
Serial quantification of BCR-ABL1 mRNA is an important therapeutic indicator in chronic myeloid leukaemia, but there is a substantial variation in results reported by different laboratories. To improve comparability, an internationally accepted plasmid certified reference material (CRM) was developed according to ISO Guide 34:2009. Fragments of BCR-ABL1 (e14a2 mRNA fusion), BCR and GUSB transcripts were amplified and cloned into pUC18 to yield plasmid pIRMM0099. Six different linearised plasmid solutions were produced with the following copy number concentrations, assigned by digital PCR, and expanded uncertainties: 1.08±0.13 × 10(6), 1.08±0.11 × 10(5), 1.03±0.10 × 10(4), 1.02±0.09 × 10(3), 1.04±0.10 × 10(2) and 10.0±1.5 copies/μl. The certification of the material for the number of specific DNA fragments per plasmid, copy number concentration of the plasmid solutions and the assessment of inter-unit heterogeneity and stability were performed according to ISO Guide 35:2006. Two suitability studies performed by 63 BCR-ABL1 testing laboratories demonstrated that this set of 6 plasmid CRMs can help to standardise a number of measured transcripts of e14a2 BCR-ABL1 and three control genes (ABL1, BCR and GUSB). The set of six plasmid CRMs is distributed worldwide by the Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements (Belgium) and its authorised distributors (https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/reference-materials/catalogue/; CRM code ERM-AD623a-f).
Figures


References
-
- Cross NC. Standardisation of molecular monitoring for chronic myeloid leukaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2009;22:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Press RD, Kamel-Reid S, Ang D. BCR–ABL1 RT-qPCR for monitoring the molecular response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15:565–576. - PubMed
-
- Branford S, Prime J. Chronic myelogenous leukemia: monitoring response to therapy. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2011;6:75–81. - PubMed
-
- Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N, et al. Standardization and quality control studies of 'real-time' quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia—a Europe Against Cancer program. Leukemia. 2003;17:2318–2357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

