Structural basis of hAT transposon end recognition by Hermes, an octameric DNA transposase from Musca domestica
- PMID: 25036632
- PMCID: PMC4105704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.037
Structural basis of hAT transposon end recognition by Hermes, an octameric DNA transposase from Musca domestica
Abstract
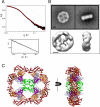
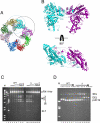
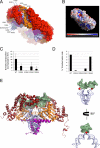
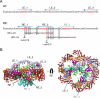
Hermes is a member of the hAT transposon superfamily that has active representatives, including McClintock's archetypal Ac mobile genetic element, in many eukaryotic species. The crystal structure of the Hermes transposase-DNA complex reveals that Hermes forms an octameric ring organized as a tetramer of dimers. Although isolated dimers are active in vitro for all the chemical steps of transposition, only octamers are active in vivo. The octamer can provide not only multiple specific DNA-binding domains to recognize repeated subterminal sequences within the transposon ends, which are important for activity, but also multiple nonspecific DNA binding surfaces for target capture. The unusual assembly explains the basis of bipartite DNA recognition at hAT transposon ends, provides a rationale for transposon end asymmetry, and suggests how the avidity provided by multiple sites of interaction could allow a transposase to locate its transposon ends amidst a sea of chromosomal DNA.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aravind L. The BED finger, a novel DNA-binding domain in chromatin-boundary-element-binding proteins and transposases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000;25:421–423. - PubMed
-
- Becker H-A, Kunze R. Maize Activator transposase has a bipartite DNA binding domain that recognizes subterminal sequences and the terminal inverted repeats. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1997;254:219–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

