What is the optimal alignment of the tibial and femoral components in knee arthroplasty?
- PMID: 25036719
- PMCID: PMC4164865
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2014.940573
What is the optimal alignment of the tibial and femoral components in knee arthroplasty?
Abstract
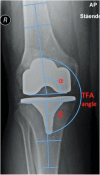
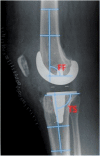
Background: Surgeon-dependent factors such as optimal implant alignment are thought to play a significant role in outcome following primary total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Exact definitions and references for optimal alignment are, however, still being debated. This overview of the literature describes different definitions of component alignment following primary TKA for (1) tibiofemoral alignment in the AP plane, (2) tibial and femoral component placement in the AP plane, (3) tibial and femoral component placement in the sagittal plane, and (4) rotational alignment of tibial and femoral components and their role in outcome and implant survival.
Methods: We performed a literature search for original and review articles on implant positioning following primary TKA. Definitions for coronal, sagittal, and rotational placement of femoral and tibial components were summarized and the influence of positioning on survival and functional outcome was considered.
Results: Many definitions exist when evaluating placement of femoral and tibial components. Implant alignment plays a role in both survival and functional outcome following primary TKA, as component malalignment can lead to increased failure rates, maltracking, and knee pain.
Interpretation: Based on currently available evidence, surgeons should aim for optimal alignment of tibial and femoral components when performing TKA.
Figures
References
-
- Akagi M, Matsusue Y, Mata T, Asada Y, Horiguchi M, Iida H, et al. Effect of rotational alignment on patellar tracking in total knee arthro... . Clin Orthop. 1999;366:155–63. - PubMed
-
- Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C. Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee ... . Clin Orthop. 2005;436:172–6. - PubMed
-
- Anouchi YS, Whiteside LA, Kaiser AD, Milliano MT. The effects of axial rotational alignment of the femoral component on kn... . Clin Orthop. 1993;287:170–7. - PubMed
-
- Arima J, Whiteside LA, McCarthy DS, White SE. Femoral rotational alignment, based on the anteroposterior axis, in tota... . J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1995;77(9):1331–4. - PubMed
-
- Baker PN, Deehan DJ, Lees D, Jameson S, Avery PJ, Gregg PJ, et al. The effect of surgical factors on early patient-reported outcome measure... . J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2012;94(8):1058–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
