Identifying and quantifying heterogeneity in high content analysis: application of heterogeneity indices to drug discovery
- PMID: 25036749
- PMCID: PMC4103836
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102678
Identifying and quantifying heterogeneity in high content analysis: application of heterogeneity indices to drug discovery
Erratum in
-
Correction: Identifying and quantifying heterogeneity in high content analysis: application of heterogeneity indices to drug discovery.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0120468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120468. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781996 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
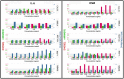
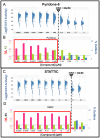
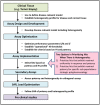
One of the greatest challenges in biomedical research, drug discovery and diagnostics is understanding how seemingly identical cells can respond differently to perturbagens including drugs for disease treatment. Although heterogeneity has become an accepted characteristic of a population of cells, in drug discovery it is not routinely evaluated or reported. The standard practice for cell-based, high content assays has been to assume a normal distribution and to report a well-to-well average value with a standard deviation. To address this important issue we sought to define a method that could be readily implemented to identify, quantify and characterize heterogeneity in cellular and small organism assays to guide decisions during drug discovery and experimental cell/tissue profiling. Our study revealed that heterogeneity can be effectively identified and quantified with three indices that indicate diversity, non-normality and percent outliers. The indices were evaluated using the induction and inhibition of STAT3 activation in five cell lines where the systems response including sample preparation and instrument performance were well characterized and controlled. These heterogeneity indices provide a standardized method that can easily be integrated into small and large scale screening or profiling projects to guide interpretation of the biology, as well as the development of therapeutics and diagnostics. Understanding the heterogeneity in the response to perturbagens will become a critical factor in designing strategies for the development of therapeutics including targeted polypharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Li RX, Zeng R (2009) Dynamic proteomics for investigating the response of individual cancer cells under drug action. Expert Rev Proteomics 6: 19–21. - PubMed
-
- Almendro V, Marusyk A, Polyak K (2013) Cellular Heterogeneity and Molecular Evolution in Cancer. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 8: 277–302. - PubMed
-
- Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ (2013) Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature 501: 346–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

