Rho GTPases modulate malignant transformation of tumor cells
- PMID: 25036871
- PMCID: PMC4125382
- DOI: 10.4161/sgtp.29019
Rho GTPases modulate malignant transformation of tumor cells
Abstract
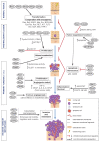
Rho GTPases are involved in the acquisition of all the hallmarks of cancer, which comprise 6 biological capabilities acquired during the development of human tumors. The hallmarks include proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis programs, as defined by Hanahan and Weinberg. (1) Controlling these hallmarks are genome instability and inflammation. Emerging hallmarks are reprogramming of energy metabolism and evading immune destruction. To give a different view to the readers, we will not be focusing on invasion, metastasis, or cytoskeletal remodeling, but we will review here how Rho GTPases contribute to other hallmarks of cancer with a special emphasis on malignant transformation.
Keywords: Rho GTPases; inflammation; metabolism; oncogene; proliferation; senescence; survival; transformation; tumor progression.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
