Inflammation, Cancer and Oxidative Lipoxygenase Activity are Intimately Linked
- PMID: 25037020
- PMCID: PMC4190552
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers6031500
Inflammation, Cancer and Oxidative Lipoxygenase Activity are Intimately Linked
Abstract
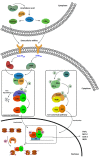
Cancer and inflammation are intimately linked due to specific oxidative processes in the tumor microenvironment. Lipoxygenases are a versatile class of oxidative enzymes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism. An increasing number of arachidonic acid metabolites is being discovered and apart from their classically recognized pro-inflammatory effects, anti-inflammatory effects are also being described in recent years. Interestingly, these lipid mediators are involved in activation of pro-inflammatory signal transduction pathways such as the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, which illustrates the intimate link between lipid signaling and transcription factor activation. The identification of the role of arachidonic acid metabolites in several inflammatory diseases led to a significant drug discovery effort around arachidonic acid metabolizing enzymes. However, to date success in this area has been limited. This might be attributed to the lack of selectivity of the developed inhibitors and to a lack of detailed understanding of the functional roles of arachidonic acid metabolites in inflammatory responses and cancer. This calls for a more detailed investigation of the activity of arachidonic acid metabolizing enzymes and development of more selective inhibitors.
Figures



References
-
- Nowsheen K., Aziz T.B., Kryston N.F., Ferguson N.F., Georgakilas A. The interplay between inflammation and oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012;12:672–680. - PubMed
-
- Haining J.L., Axelrod B. Induction period in the lipoxidase-catalyzed oxidation of linoleic acid and its abolition by substrate peroxide. J. Biol. Chem. 1958;232:193–202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

