Tuberculosis in children
- PMID: 25037105
- PMCID: PMC4143109
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017855
Tuberculosis in children
Abstract
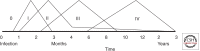
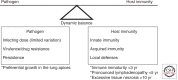
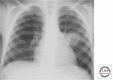
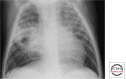
Many clinicians regard tuberculosis as an adult pulmonary disease, but tuberculosis (TB) is a major cause of disease, both pulmonary and extrapulmonary, and death in young children from TB-endemic countries, especially in areas affected by poverty, social disruption, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. This article reviews the disease burden and the natural history of disease in children with TB. It also provides guidance regarding the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of TB in children.
Copyright © 2014 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
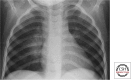
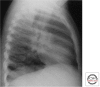
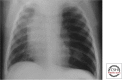
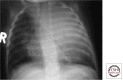
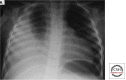
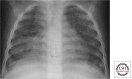
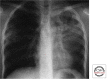

References
-
- Abubakar I, Ford N, Cox H 2013. The rising tide of drug-resistant tuberculosis—Time for visionary political leadership. Lancet Infect Dis 13: 529–539 - PubMed
-
- Amanullah F, Ashfaq M, Khowaja S, Parekh A, Salahuddin N, Lotia-Farrukh I, Khan A, Becerra MC 2014. High tuberculosis prevalence in children exposed at home to drug-resistant tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 18: 520–527 - PubMed
-
- Andronikou S, van Hoenacker FM, de Backer AI 2009. Advances in imaging chest tuberculosis: Blurring-of-differences-between-children-and-adults. Clin Chest Med 30: 717–744 - PubMed
-
- Bates M, Mudenda V, Mwaba P, Zumla A 2013. Deaths due to respiratory tract infections in Africa: A review of autopsy studies. Curr Opin Pulm Med 19: 229–237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
