Mitochondrial myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia (MLASA) plus associated with a novel de novo mutation (m.8969G>A) in the mitochondrial encoded ATP6 gene
- PMID: 25037980
- PMCID: PMC4253070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.06.004
Mitochondrial myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia (MLASA) plus associated with a novel de novo mutation (m.8969G>A) in the mitochondrial encoded ATP6 gene
Abstract
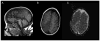
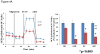
Mitochondrial myopathy, lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia (MLASA) is a rare mitochondrial disorder that has previously been associated with mutations in PUS1 and YARS2. In the present report, we describe a 6-year old male with an MLASA plus phenotype. This patient had features of MLASA in the setting of developmental delay, sensorineural hearing loss, epilepsy, agenesis of the corpus callosum, failure to thrive, and stroke-like episodes. Sequencing of the mitochondrial genome identified a novel de novo, heteroplasmic mutation in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encoded ATP6 gene (m.8969G>A, p.S148N). Whole exome sequencing did not identify mutations or variants in PUS1 or YARS2 or any known nuclear genes that could affect mitochondrial function and explain this phenotype. Studies of fibroblasts derived from the patient revealed a decrease in oligomycin-sensitive respiration, a finding which is consistent with a complex V defect. Thus, this mutation in MT-ATP6 may represent the first mtDNA point mutation associated with the MLASA phenotype.
Keywords: ATP6; Lactic acidosis; MLASA; Mitochondria; Mitochondrial myopathy.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Casas K, Bykhovskaya Y, Mengesha E, Wang D, Yang H, Taylor K, Inbal A, Fischel-Ghodsian N. Gene responsible for mitochondrial myopathy and sideroblastic anemia (MSA) maps to chromosome 12q24.33. American journal of medical genetics Part A. 2004;127A:44–49. - PubMed
-
- Riley LG, Cooper S, Hickey P, Rudinger-Thirion J, McKenzie M, Compton A, Lim SC, Thorburn D, Ryan MT, Giege R, Bahlo M, Christodoulou J. Mutation of the mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase gene, YARS2, causes myopathy, lactic acidosis, and sideroblastic anemia--MLASA syndrome. American journal of human genetics. 2010;87:52–59. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeharia A, Fischel-Ghodsian N, Casas K, Bykhocskaya Y, Tamari H, Lev D, Mimouni M, Lerman-Sagie T. Mitochondrial myopathy, sideroblastic anemia, and lactic acidosis: an autosomal recessive syndrome in Persian Jews caused by a mutation in the PUS1 gene. Journal of child neurology. 2005;20:449–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

