A novel device for target controlled administration and reflection of desflurane--the Mirus™
- PMID: 25040673
- PMCID: PMC4303981
- DOI: 10.1111/anae.12798
A novel device for target controlled administration and reflection of desflurane--the Mirus™
Abstract
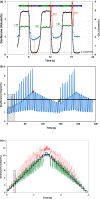
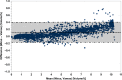
The Anaconda™ system is used to deliver inhalational sedation in the intensive care unit in mainland Europe. The new Mirus™ system also uses a reflector like the Anaconda; however, it also identifies end-tidal concentrations from the gas flow, injects anaesthetics during early inspiration, controls anaesthetic concentrations automatically, and can be used with desflurane, which is not possible using the Anaconda. We tested the Mirus with desflurane in the laboratory. Compared with an external gas monitor, the bias (two standard deviations) of the end-tidal concentration was 0.11 (0.29)% volume. In addition, automatic control was reasonable and maximum concentration delivered was 10.2%, which was deemed to be sufficient for clinical use. Efficiency was > 80% and was also deemed to be acceptable, but only when delivering a low concentration of desflurane (≤ 1.8%). By modifying the reflector, we improved efficiency up to a concentration of 3.6%. The Mirus appears to be a promising new device for long-term sedation with desflurane on the intensive care unit, but efficiency must be improved before routine clinical use becomes affordable.
© 2014 The Authors. Anaesthesia published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures



References
-
- Sackey PV, Martling CR, Granath F, Radell PJ. Prolonged isoflurane sedation of intensive care unit patients with the Anesthetic Conserving Device. Critical Care Medicine. 2004;32:2241–6. - PubMed
-
- Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Critical Care Medicine. 2013;41:263–306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

