Heart failure and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 25041352
- PMCID: PMC4409079
- DOI: 10.1111/joim.12287
Heart failure and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
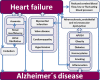
It has recently been proposed that heart failure is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease. Decreased cerebral blood flow and neurohormonal activation due to heart failure may contribute to the dysfunction of the neurovascular unit and cause an energy crisis in neurons. This leads to the impaired clearance of amyloid beta and hyperphosphorylation of tau protein, resulting in the formation of amyloid beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. In this article, we will summarize the current understanding of the relationship between heart failure and Alzheimer's disease based on epidemiological studies, brain imaging research, pathological findings and the use of animal models. The importance of atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, blood pressure and valve disease as well as the effect of relevant medications will be discussed.
Keywords: Alzheimer′s disease; dementia; heart failure; neurocardiology; neurovascular unit.
© 2014 The Authors. Journal of Internal Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Association for the Publication of the Journal of Internal Medicine.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cardiovascular system participation in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.J Intern Med. 2015 Apr;277(4):426-8. doi: 10.1111/joim.12311. Epub 2014 Oct 20. J Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 25251680 No abstract available.
References
-
- Prince M, Bryce R, Albanese E, Wimo A, Ribeiro W, Ferri CP. The global prevalence of dementia: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:63–75.e2. - PubMed
-
- Wimo A, Jonsson L, Bond J, Prince M, Winblad B Alzheimer Disease International. The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:1–11.e3. - PubMed
-
- Wallin K, Bostrom G, Kivipelto M, Gustafson Y. Risk factors for incident dementia in the very old. Int Psychogeriatr. 2013;25:1135–43. - PubMed
-
- Kivipelto M, Ngandu T, Fratiglioni L, et al. Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1556–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

