Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
- PMID: 25043025
- PMCID: PMC4244910
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13393
Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Abstract
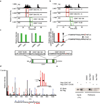
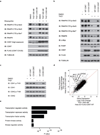
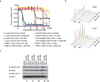
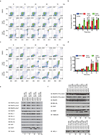
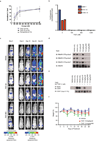
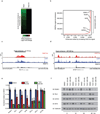
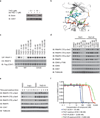
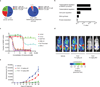
Tumour oncogenes include transcription factors that co-opt the general transcriptional machinery to sustain the oncogenic state, but direct pharmacological inhibition of transcription factors has so far proven difficult. However, the transcriptional machinery contains various enzymatic cofactors that can be targeted for the development of new therapeutic candidates, including cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Here we present the discovery and characterization of a covalent CDK7 inhibitor, THZ1, which has the unprecedented ability to target a remote cysteine residue located outside of the canonical kinase domain, providing an unanticipated means of achieving selectivity for CDK7. Cancer cell-line profiling indicates that a subset of cancer cell lines, including human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL), have exceptional sensitivity to THZ1. Genome-wide analysis in Jurkat T-ALL cells shows that THZ1 disproportionally affects transcription of RUNX1 and suggests that sensitivity to THZ1 may be due to vulnerability conferred by the RUNX1 super-enhancer and the key role of RUNX1 in the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of these tumour cells. Pharmacological modulation of CDK7 kinase activity may thus provide an approach to identify and treat tumour types that are dependent on transcription for maintenance of the oncogenic state.
Figures





Comment in
-
Inhibit globally, act locally: CDK7 inhibitors in cancer therapy.Cancer Cell. 2014 Aug 11;26(2):158-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.020. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 25117707
References
-
- O'Neil J, Look AT. Mechanisms of transcription factor deregulation in lymphoid cell transformation. Oncogene. 2007;26:6838–6849. - PubMed
-
- Berg T. Inhibition of transcription factors with small organic molecules. Current opinion in chemical biology. 2008;12:464–471. - PubMed
-
- Lu Q, et al. Perspectives on the discovery of small-molecule modulators for epigenetic processes. Journal of biomolecular screening. 2012;17:555–571. - PubMed
-
- Patricelli MP, et al. Functional interrogation of the kinome using nucleotide acyl phosphates. Biochemistry. 2007;46:350–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 CA130876-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006097/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA179483/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS047572/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006097-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA178860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA178860-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA109901/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA130876/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS047572-10/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

