Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer
- PMID: 25043058
- PMCID: PMC4184286
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13540
Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer.Nature. 2015 Apr 16;520(7547):388. doi: 10.1038/nature14304. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25739500 No abstract available.
Abstract
Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) is an autocrine/paracrine regulator whose binding to heparan sulphate proteoglycans effectively precludes its circulation. Although FGF1 is known as a mitogenic factor, FGF1 knockout mice develop insulin resistance when stressed by a high-fat diet, suggesting a potential role in nutrient homeostasis. Here we show that parenteral delivery of a single dose of recombinant FGF1 (rFGF1) results in potent, insulin-dependent lowering of glucose levels in diabetic mice that is dose-dependent but does not lead to hypoglycaemia. Chronic pharmacological treatment with rFGF1 increases insulin-dependent glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and suppresses the hepatic production of glucose to achieve whole-body insulin sensitization. The sustained glucose lowering and insulin sensitization attributed to rFGF1 are not accompanied by the side effects of weight gain, liver steatosis and bone loss associated with current insulin-sensitizing therapies. We also show that the glucose-lowering activity of FGF1 can be dissociated from its mitogenic activity and is mediated predominantly via FGF receptor 1 signalling. Thus we have uncovered an unexpected, neomorphic insulin-sensitizing action for exogenous non-mitogenic human FGF1 with therapeutic potential for the treatment of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
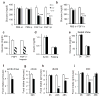

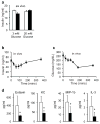




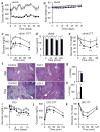
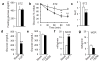
Comment in
-
Therapy: FGF1 restores blood glucose levels and insulin sensitivity in diabetic mice.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014 Oct;10(10):576. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.129. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25069461 No abstract available.
-
Obesity and diabetes: FGF1 goes long to tackle diabetes.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Sep;13(9):652-3. doi: 10.1038/nrd4419. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25176429 No abstract available.
-
Break on through to the other 1.Cell Metab. 2014 Oct 7;20(4):554-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.09.009. Cell Metab. 2014. PMID: 25295781
References
-
- Lehrke M, Lazar MA. The many faces of PPARgamma. Cell. 2005;123:993–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK054441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK-007494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54-HD-012303-25/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DE13686/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DK-074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-DK054441-14A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

