PLXNA4 is associated with Alzheimer disease and modulates tau phosphorylation
- PMID: 25043464
- PMCID: PMC4830273
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.24219
PLXNA4 is associated with Alzheimer disease and modulates tau phosphorylation
Abstract
Objective: Much of the genetic basis for Alzheimer disease (AD) is unexplained. We sought to identify novel AD loci using a unique family-based approach that can detect robust associations with infrequent variants (minor allele frequency < 0.10).
Methods: We conducted a genome-wide association study in the Framingham Heart Study (discovery) and NIA-LOAD (National Institute on Aging-Late-Onset Alzheimer Disease) Study (replication) family-based cohorts using an approach that accounts for family structure and calculates a risk score for AD as the outcome. Links between the most promising gene candidate and AD pathogenesis were explored in silico as well as experimentally in cell-based models and in human brain.
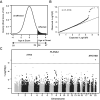
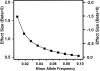
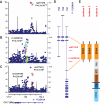
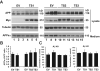
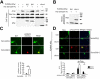
Results: Genome-wide significant association was identified with a PLXNA4 single nucleotide polymorphism (rs277470) located in a region encoding the semaphorin-3A (SEMA3A) binding domain (meta-analysis p value [meta-P] = 4.1 × 10(-8) ). A test for association with the entire region was also significant (meta-P = 3.2 × 10(-4) ). Transfection of SH-SY5Y cells or primary rat neurons with full-length PLXNA4 (TS1) increased tau phosphorylation with stimulated by SEMA3A. The opposite effect was observed when cells were transfected with shorter isoforms (TS2 and TS3). However, transfection of any isoform into HEK293 cells stably expressing amyloid β (Aβ) precursor protein (APP) did not result in differential effects on APP processing or Aβ production. Late stage AD cases (n = 9) compared to controls (n = 5) had 1.9-fold increased expression of TS1 in cortical brain tissue (p = 1.6 × 10(-4) ). Expression of TS1 was significantly correlated with the Clinical Dementia Rating score (ρ = 0.75, p = 2.2 × 10(-4) ), plaque density (ρ = 0.56, p = 0.01), and Braak stage (ρ = 0.54, p = 0.02).
Interpretation: Our results indicate that PLXNA4 has a role in AD pathogenesis through isoform-specific effects on tau phosphorylation.
© 2014 American Neurological Association.
Figures


References
-
- Thies W, Bleiler L. 2011 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2011 Mar;7(2):208–44. - PubMed
-
- Farrer LA. Genetics and the dementia patient. Neurologist. 1997;3:13–30.
-
- Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. Jama. 1997 Oct 22–29;278(16):1349–56. - PubMed
-
- Lill CM, Bertram L. Towards unveiling the genetics of neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Neurol. 2012 Nov;31(5):531–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PG30-AG13846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG000001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24-AG26395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG025259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24-AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG0001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

