Liver injury from herbals and dietary supplements in the U.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network
- PMID: 25043597
- PMCID: PMC4293199
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.27317
Liver injury from herbals and dietary supplements in the U.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network
Abstract
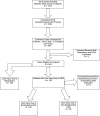
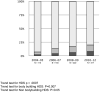
The Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN) studies hepatotoxicity caused by conventional medications as well as herbals and dietary supplements (HDS). To characterize hepatotoxicity and its outcomes from HDS versus medications, patients with hepatotoxicity attributed to medications or HDS were enrolled prospectively between 2004 and 2013. The study took place among eight U.S. referral centers that are part of the DILIN. Consecutive patients with liver injury referred to a DILIN center were eligible. The final sample comprised 130 (15.5%) of all subjects enrolled (839) who were judged to have experienced liver injury caused by HDS. Hepatotoxicity caused by HDS was evaluated by expert opinion. Demographic and clinical characteristics and outcome assessments, including death and liver transplantation (LT), were ascertained. Cases were stratified and compared according to the type of agent implicated in liver injury; 45 had injury caused by bodybuilding HDS, 85 by nonbodybuilding HDS, and 709 by medications. Liver injury caused by HDS increased from 7% to 20% (P < 0.001) during the study period. Bodybuilding HDS caused prolonged jaundice (median, 91 days) in young men, but did not result in any fatalities or LT. The remaining HDS cases presented as hepatocellular injury, predominantly in middle-aged women, and, more frequently, led to death or transplantation, compared to injury from medications (13% vs. 3%; P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The proportion of liver injury cases attributed to HDS in DILIN has increased significantly. Liver injury from nonbodybuilding HDS is more severe than from bodybuilding HDS or medications, as evidenced by differences in unfavorable outcomes (death and transplantation). (Hepatology 2014;60:1399-1408).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00345930.
© 2014 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Picciano MF, Dwyer JT, Radimer KL, et al. Dietary supplement use among infants, children, and adolescents in the United States, 1999-2002. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2007;161(10):978–985. - PubMed
-
- Radimer K, Bindewald B, Hughes J, Ervin B, Swanson C, Picciano MF. Dietary supplement use by US adults: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2000. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;160(4):339–349. - PubMed
-
- Bailey RL, Gahche JJ, Miller PE, Thomas PR, Dwyer JT. Why US adults use dietary supplements. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(5):355–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
