Midregional pro-adrenomedullin plasma concentrations are blunted in severe preeclampsia
- PMID: 25043691
- PMCID: PMC4143458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2014.07.003
Midregional pro-adrenomedullin plasma concentrations are blunted in severe preeclampsia
Abstract
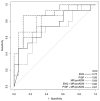
Levels of the peptide hormone adrenomedullin (AM) are elevated during normal pregnancy, but whether this differs during complications of pregnancy remains unresolved. AM can be quantified by measuring its pre-prohormone byproduct, midregional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proADM). MR-proADM has shown prognostic value as a biomarker of heart failure, sepsis, and community-acquired pneumonia. Given the relevance of AM to pregnancy, we tested the hypothesis that MR-proADM provides a biomarker for preeclampsia. We find that MR-proADM plasma concentrations are blunted in severe preeclampsia and that MR-proADM is similarly effective as established biomarkers endoglin and placental growth factor at discriminating patients with severe preeclampsia from controls.
Keywords: Adrenomedullin; Midregional pro-adrenomedullin; Preeclampsia; Pregnancy.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ, Pijnenborg R. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2010;376(9741):631–44. - PubMed
-
- Gibbons C, Dackor R, Dunworth W, Fritz-Six K, Caron KM. Receptor activity-modifying proteins: RAMPing up adrenomedullin signaling. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(4):783–96. - PubMed
-
- Pijnenborg R, Vercruysse L, Hanssens M. The uterine spiral arteries in human pregnancy: facts and controversies. Placenta. 2006;27(9-10):939–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

