Serum Levels of Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor in Infants with Late-onset Sepsis
- PMID: 25043869
- PMCID: PMC6806707
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21777
Serum Levels of Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor in Infants with Late-onset Sepsis
Abstract
Background: Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) has been studied in a variety of diseases. The aim of the study is to investigate the levels of suPAR in neonates with sepsis.
Methods: The infants enrolled to this prospective study were classified into four groups. Group 1, 2, and 3 were referred as the patient groups (40 infants), and group 4 was referred as control group (26 infants). Blood samples for whole blood count, C-reactive protein (CRP), suPAR and blood culture were obtained before initiating antimicrobial therapy, and two further samples were obtained on day 3 and at the end of the treatment for CRP and suPAR.
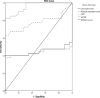
Results: The mean gestational ages of patient and control groups was similar. The median level of initial suPAR was 18.8 ng/mL (range 6.8-30.1 ng/mL) in the patient groups, and 6.0 ng/mL (range 3.7-10.8 ng/mL) in the control group (P < 0.001). A significant decrease in suPAR level was observed from the inclusion to the third day and end of the treatment (P < 0.001). The area under the curve (AUC) for suPAR is 0.959 (95% Cl: 0.919-0.999) and for CRP is 0.782 (95% Cl: 0.669-0.895). At a cut-off value of 11.3 ng/mL for suPAR the specificity was 100%, and the sensitivity was 82.5%. There was a positive correlation between laboratory values of CRP and suPAR (r: 0.359, P = 0.003).
Conclusion: This is the first study that investigated the levels of suPAR in neonates and our results demonstrate that suPAR is a powerful marker of inflammation in infants with sepsis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01294865.
Keywords: marker; neonate; sepsis; soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor; urokinase plasminogen activator receptor.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Ng PC, Lam HS. Diagnostic markers for neonatal sepsis. Curr Opin Pediatr 2006;18:125–131. - PubMed
-
- Ng PC. Clinical trials for evaluating diagnostic markers of infection in neonates. Biol Neonate 2005;87:111–112. - PubMed
-
- Remington JS, Klein JO, editors. Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. WB Saunders Company, Philadephia; 2001.
-
- Arnon S, Litmanovitz I. Diagnostic tests in neonatal sepsis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2008;21:223–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

