Functional roles of Syk in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses
- PMID: 25045209
- PMCID: PMC4090447
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/270302
Functional roles of Syk in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses
Abstract
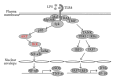
Inflammation is a series of complex biological responses to protect the host from pathogen invasion. Chronic inflammation is considered a major cause of diseases, such as various types of inflammatory/autoimmune diseases and cancers. Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) was initially found to be highly expressed in hematopoietic cells and has been known to play crucial roles in adaptive immune responses. However, recent studies have reported that Syk is also involved in other biological functions, especially in innate immune responses. Although Syk has been extensively studied in adaptive immune responses, numerous studies have recently presented evidence that Syk has critical functions in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses and is closely related to innate immune response. This review describes the characteristics of Syk-mediated signaling pathways, summarizes the recent findings supporting the crucial roles of Syk in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses and diseases, and discusses Syk-targeted drug development for the therapy of inflammatory diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Kaur M, Singh M, Silakari O. Inhibitors of switch kinase “spleen tyrosine kinase” in inflammation and immune-mediated disorders: a review. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2013;67:434–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous