The study of naphthoquinones and their complexes with DNA by using Raman spectroscopy and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: new insight into interactions of DNA with plant secondary metabolites
- PMID: 25045679
- PMCID: PMC4090563
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/461393
The study of naphthoquinones and their complexes with DNA by using Raman spectroscopy and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: new insight into interactions of DNA with plant secondary metabolites
Abstract
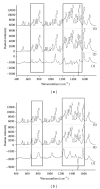
Naphthoquinones represent the group of plant secondary metabolites with cytotoxic properties based on their ability to generate reactive oxygen species and interfere with the processes of cell respiration. Due to this fact, the possible cytotoxic mechanisms on cellular and subcellular levels are investigated intensively. There are many targets of cytotoxic action on the cellular level; however, DNA is a critical target of many cytotoxic compounds. Due to the cytotoxic properties of naphthoquinones, it is necessary to study the processes of naphthoquinones, DNA interactions (1,4-naphthoquinone, binapthoquinone, juglone, lawsone, plumbagin), especially by using modern analytical techniques. In our work, the Raman spectroscopy was used to determine the possible binding sites of the naphthoquinones on the DNA and to characterize the bond of naphthoquinone to DNA. Experimental data reveals the relationships between the perturbations of structure-sensitive Raman bands and the types of the naphthoquinones involved. The modification of DNA by the studied naphthoquinones leads to the nonspecific interaction, which causes the transition of B-DNA into A-DNA conformation. The change of the B-conformation of DNA for all measured DNA modified by naphthoquinones except plumbagin is obvious.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of cytotoxic plant naphthoquinones, juglone, plumbagin, lawsone and 2-methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii reveals the biochemical mechanism of juglone toxicity by rapid depletion of plastoquinol.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023 Apr;197:107660. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107660. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36996637
-
1,4-Naphthoquinones as inducers of oxidative damage and stress signaling in HaCaT human keratinocytes.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Apr 15;496(2):93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.02.002. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20153715
-
Cytotoxicity of naphthoquinones and their capacity to generate reactive oxygen species is quenched when conjugated with gold nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:2113-22. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S24074. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 22114475 Free PMC article.
-
[Naphthoquinones and their pharmacological properties].Ceska Slov Farm. 2007 Jun;56(3):114-20. Ceska Slov Farm. 2007. PMID: 17867522 Review. Czech.
-
Iron and its complexation by phenolic cellular metabolites: from oxidative stress to chemical weapons.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Jan;5(1):4-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.1.10197. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20592800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid discrimination between wild and cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis through comparative analysis of label-free SERS technique and mass spectrometry.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Aug 14;9:100820. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100820. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39263205 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Inhibition of Hsp90 Protein by Benzothiazoloquinazolinequinones Is Enhanced in The Presence of Ascorbate. A Preliminary In Vivo Antiproliferative Study.Molecules. 2020 Feb 20;25(4):953. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040953. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32093392 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Changes Induced by Quinones: High-Resolution Microwave Study of 1,4-Naphthoquinone.Chemphyschem. 2020 Dec 2;21(23):2579-2584. doi: 10.1002/cphc.202000665. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Chemphyschem. 2020. PMID: 32954594 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of L-fucoside from lapachol-loaded nanoemulsion as a strategy to breast cancer treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:116054. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116054. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38150876 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Naphthazarin (DHNQ) Combined with Lawsone (NQ-2-OH) or 1,4-Naphthoquinone (NQ) on the Auxin-Induced Growth of Zea mays L. Coleoptile Segments.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 11;20(7):1788. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071788. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30978914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakunphueak A, Panichayupakaranant P. Effects of donor plants and plant growth regulators on naphthoquinone production in root cultures of Impatiens balsamina. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture. 2010;102(1):9–15.
-
- Babula P, Adam V, Havel L, Kizek R. Noteworthy secondary metabolites naphthoquinones—their occurrence, pharmacological properties and analysis. Current Pharmaceutical Analysis. 2009;5(1):47–68.
-
- Babula P, Huska D, Hanustiak P, et al. Flow injection analysis coupled with carbon electrodes as the tool for analysis of naphthoquinones with respect to their content and functions in biological samples. Sensors. 2006;6(11):1466–1482.
-
- Babula P, Mikelová R, Adam V, et al. Chromatographic analysis of naphthoquinones in plants. Chemicke Listy. 2006;100(4):271–276.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

