A randomized, placebo-controlled trial to determine the course of aminotransferase elevation during prolonged acetaminophen administration
- PMID: 25047090
- PMCID: PMC4118644
- DOI: 10.1186/2050-6511-15-39
A randomized, placebo-controlled trial to determine the course of aminotransferase elevation during prolonged acetaminophen administration
Abstract
Background: Acetaminophen administration for more than 4 days causes aminotransferase elevation in some subjects. The objective of this randomized, placebo-controlled trial is to describe the course of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation in subjects administered 4 g/day of acetaminophen for at least 16 days.
Methods: A randomized, placebo controlled trial of acetaminophen (4 g/day) vs placebo. Subjects were healthy volunteers with normal liver enzymes. The primary outcome was the course of ALT during acetaminophen administration. All subjects were treated for a minimum of 16 days. Subjects with ALT elevation at day 16 were continued on treatment until these elevations resolved up to a maximum of 40 days. Subjects were also evaluated for elevation of INR or serum bilirubin as evidence of hepatic dysfunction.
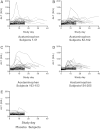
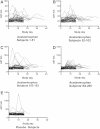
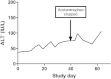
Results: 157/205 (77%) completed acetaminophen subjects had no ALT elevation or transient elevations that resolved by day 16. Of the 48 subjects who had ALT elevations at study day 16, 47 continued on acetaminophen and had resolution by study day 40. One acetaminophen subject did not have resolution by study day 40, and the course of aminotransferase elevation suggests an alternative cause. One placebo subject had an ALT elevation at day 16 that resolved by day 22. The highest observed ALT among all acetaminophen subjects was 191 IU/L. The mean ALT at day 16 was 4.4 IU/L higher for the acetaminophen than for the placebo group. No subject developed liver dysfunction.
Conclusions: A minority of subjects treated with 4 g/day of acetaminophen for 16 days will have low-grade aminotransferase elevations that are not accompanied by liver dysfunction and resolve if administration is continued.
Trials registration: Clintrials.gov NCT00743093 registered August 26, 2008.
Figures

References
-
- Dart RC, Bailey E. Does therapeutic use of acetaminophen cause acute liver failure? Pharmacotherapy. 2007;27:1219–1230. - PubMed
-
- Harrill AH, Watkins PB, Su S, Ross PK, Harbourt DE, Stylianou IM, Boorman GA, Russo MW, Sackler RS, Harris SC, Smith PC, Tennant R, Bogue M, Paigen K, Harris C, Contractor T, Wiltshire T, Rusyn I, Threadgill DW. Mouse population-guided resequencing reveals that variants in CD44 contribute to acetaminophen-induced liver injury in humans. Genome Res. 2009;19:1507–1515. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heard K, Green JL, Bailey JE, Bogdan GM, Dart RC. A randomized trial to determine the change in alanine aminotransferase during 10 days of paracetamol (acetaminophen) administration in subjects who consume moderate amounts of alcohol. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:283–290. - PubMed
-
- Parra D, Beckey NP, Stevens GR. The effect of acetaminophen on the international normalized ratio in patients stabilized on warfarin therapy. Pharmacotherapy. 2007;27:675–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

