SC-2001 overcomes STAT3-mediated sorafenib resistance through RFX-1/SHP-1 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25047655
- PMCID: PMC4198826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.06.005
SC-2001 overcomes STAT3-mediated sorafenib resistance through RFX-1/SHP-1 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
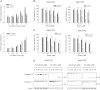
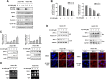
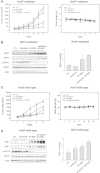
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the fifth most common solid cancer worldwide. Sorafenib, a small multikinase inhibitor, is the only approved therapy for advanced HCC. The clinical benefit of sorafenib is offset by the acquisition of sorafenib resistance. Understanding of the molecular mechanism of STAT3 overexpression in sorafenib resistance is critical if the clinical benefits of this drug are to be improved. In this study, we explored our hypothesis that loss of RFX-1/SHP-1 and further increase of p-STAT3 as a result of sorafenib treatment induces sorafenib resistance as a cytoprotective response effect, thereby, limiting sorafenib sensitivity and efficiency. We found that knockdown of RFX-1 protected HCC cells against sorafenib-induced cell apoptosis and SHP-1 activity was required for the process. SC-2001, a molecule with similar structure to obatoclax, synergistically suppressed tumor growth when used in combination with sorafenib in vitro and overcame sorafenib resistance through up-regulating RFX-1 and SHP-1 resulting in tumor suppression and mediation of dephosphorylation of STAT3. In addition, sustained sorafenib treatment in HCC led to increased p-STAT3 which was a key mediator of sorafenib sensitivity. The combination of SC-2001 and sorafenib strongly inhibited tumor growth in both wild-type and sorafenib-resistant HCC cell bearing xenograft models. These results demonstrate that inactivation of RFX/SHP-1 induced by sustained sorafenib treatment confers sorafenib resistance to HCC through p-STAT3 up-regulation. These effects can be overcome by SC-2001 through RFX-1/SHP-1 dependent p-STAT3 suppression. In conclusion, the use of SC-2001 in combination with sorafenib may constitute a new strategy for HCC therapy.
Copyright © 2014 Neoplasia Press, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bruix J., Llovet J.M. HCC surveillance: who is the target population? Hepatology. 2003;37:507–509. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., Di Bisceglie A.M., Bruix J., Kramer B.S., Lencioni R., Zhu A.X., Sherman M., Schwartz M., Lotze M., Talwalkar J. Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:698–711. - PubMed
-
- Di Maio M., Daniele B., Perrone F. Targeted therapies: Role of sorafenib in HCC patients with compromised liver function. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:505–506. - PubMed
-
- Panka D.J., Wang W., Atkins M.B., Mier J.W. The Raf inhibitor BAY 43-9006 (Sorafenib) induces caspase-independent apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1611–1619. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm S.M., Carter C., Tang L., Wilkie D., McNabola A., Rong H., Chen C., Zhang X., Vincent P., McHugh M. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7099–7109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

