Early sedation and clinical outcomes of mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective multicenter cohort study
- PMID: 25047960
- PMCID: PMC4223597
- DOI: 10.1186/cc13995
Early sedation and clinical outcomes of mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective multicenter cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Sedation overuse is frequent and possibly associated with poor outcomes in the intensive care unit (ICU) patients. However, the association of early oversedation with clinical outcomes has not been thoroughly evaluated. The aim of this study was to assess the association of early sedation strategies with outcomes of critically ill adult patients under mechanical ventilation (MV).
Methods: A secondary analysis of a multicenter prospective cohort conducted in 45 Brazilian ICUs, including adult patients requiring ventilatory support and sedation in the first 48 hours of ICU admissions, was performed. Sedation depth was evaluated after 48 hours of MV. Multivariate analysis was used to identify variables associated with hospital mortality.
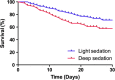
Results: A total of 322 patients were evaluated. Overall, ICU and hospital mortality rates were 30.4% and 38.8%, respectively. Deep sedation was observed in 113 patients (35.1%). Longer duration of ventilatory support was observed (7 (4 to 10) versus 5 (3 to 9) days, P = 0.041) and more tracheostomies were performed in the deep sedation group (38.9% versus 22%, P = 0.001) despite similar PaO2/FiO2 ratios and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) severity. In a multivariate analysis, age (Odds Ratio (OR) 1.02; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.00 to 1.03), Charlson Comorbidity Index >2 (OR 2.06; 95% CI, 1.44 to 2.94), Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 (SAPS 3) score (OR 1.02; CI 95%, 1.00 to 1.04), severe ARDS (OR 1.44; CI 95%, 1.09 to 1.91) and deep sedation (OR 2.36; CI 95%, 1.31 to 4.25) were independently associated with increased hospital mortality.
Conclusions: Early deep sedation is associated with adverse outcomes and constitutes an independent predictor of hospital mortality in mechanically ventilated patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Correlation of early over-sedation with clinical outcomes in mechanically ventilated patients: further studies are needed.Crit Care. 2014 Nov 14;18(6):597. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0597-7. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 25672917 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Puntillo KA, Max A, Timsit JF, Vignoud L, Chanques G, Robleda G, Roche-Campo F, Mancebo J, Divatia JV, Soares M, Ionescu DC, Grintescu IM, Vasiliu IL, Maggiore SM, Rusinova K, Owczuk R, Egerod I, Papathanassoglou ED, Kyranou M, Joynt GM, Burghi G, Freebairn RC, Ho KM, Kaarlola A, Gerritsen RT, Kesecioglu J, Sulaj MM, Norrenberg M, Benoit DD, Seha MS. et al.Determinants of procedural pain intensity in the intensive care unit: the Europain Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW, Gélinas C, Dasta JF, Davidson JE, Devlin JW, Kress JP, Joffe AM, Coursin DB, Herr DL, Tung A, Robinson BR, Fontaine DK, Ramsay MA, Riker RR, Sessler CN, Pun B, Skrobik Y, Jaeschke R. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:263–306. - PubMed
-
- Arroliga AC, Thompson BT, Ancukiewicz M, Gonzales JP, Guntupalli KK, Park PK, Wiedemann HP, Anzueto A. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Use of sedatives, opioids, and neuromuscular blocking agents in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1083–1088. - PubMed
-
- Arabi Y, Haddad S, Hawes R, Moore T, Pillay M, Naidu B, Issa A, Yeni B, Grant C, Alshimemeri A. Changing sedation practices in the intensive care unit – protocol implementation, multifaceted multidisciplinary approach and teamwork. Middle East J Anesthesiol. 2007;19:429–447. - PubMed
-
- Patel RP, Gambrell M, Speroff T, Scott TA, Pun BT, Okahashi J, Strength C, Pandharipande P, Girard TD, Burgess H, Dittus RS, Bernard GR, Ely EW. Delirium and sedation in the intensive care unit: survey of behaviors and attitudes of 1384 healthcare professionals. Critical Care Med. 2009;37:825–832. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources