Effect of gestational age and birth weight on the risk of strabismus among premature infants
- PMID: 25048624
- PMCID: PMC4339677
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.946
Effect of gestational age and birth weight on the risk of strabismus among premature infants
Abstract
Importance: Strabismus causes irreversible vision loss if not detected and treated early. It is unclear whether birth weight (BW) and gestational age (GA) are risk factors for strabismus.
Objective: To estimate the effect of BW and GA on the likelihood of premature infants developing strabismus.
Design, setting, and participants: In this longitudinal cohort analysis, we monitored a group of premature children from birth to determine the proportion that developed strabismus and the timing of the first strabismus diagnosis. Multivariable Cox regression analyses assessed the relationships of BW and GA with the development of strabismus. Regression models were adjusted for other risk factors for strabismus, sociodemographic factors, and ocular comorbidities. The analysis included 38,055 otherwise healthy children born prematurely who were enrolled for more than 6 months in a nationwide US managed care network between 2001 and 2011 in communities throughout the United States.
Exposures: Birth weight less than 2000 g or GA of 32 weeks or less.
Main outcomes and measures: Hazard ratios (HRs) for strabismus with 95% CIs.
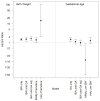
Results: Of 38,055 otherwise healthy children who were born prematurely, 583 received a diagnosis of strabismus later in life. The cumulative incidence of strabismus was 3.0% at 5 years. Controlling for GA and other covariates, infants born with BW less than 2000 g had a 61% increased hazard (HR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.22-2.13) of developing strabismus. Controlling for BW and other covariates, there was no significant association between strabismus and GA (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.69-1.38). Among premature infants with BW of less than 2000 g, a GA of 32 weeks or less conveyed no additional increased risk for developing strabismus relative to infants born after 32 weeks (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.86-1.88). In contrast, among infants with a GA of 32 weeks or less, BW of less than 2000 g conveyed a 14-fold increase in the risk of strabismus relative to BW of 2000 g or more (HR, 14.39; 95% CI, 1.99-104.14).
Conclusions and relevance: Independent of GA, very low BW conferred a large increase in strabismus risk among premature infants. In contrast, independent of BW, GA did not significantly affect the risk of strabismus. Updates to existing guidelines in the pediatric and ophthalmic literature should be considered, highlighting the importance of BW rather than GA and alerting clinicians about the need for careful monitoring of premature infants with low BW for strabismus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no proprietary or commercial interest in any material discussed in this manuscript
Figures


References
-
- Robaei D, Rose KA, Kifley A, Cosstick M, Ip JM, Mitchell P. Factors Associated with Childhood Strabismus: Findings from a Population-Based Study. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:1146–53. - PubMed
-
- Williams C, Northstone K, Howard M, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for common vision problems in children: data from the ALSPAC study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92:959–64. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Ophthalmology. Preferred Practice Patterns: Esotropia and Exotropia. San Francisco, CA: American Academy of Ophthalmology; 2012. Preferred Practice Patterns Committee. Pediatric Ophthalmology/Strabismus Panel.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

