Outcomes of children with BCR-ABL1–like acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with risk-directed therapy based on the levels of minimal residual disease
- PMID: 25049327
- PMCID: PMC4162497
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.55.4105
Outcomes of children with BCR-ABL1–like acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with risk-directed therapy based on the levels of minimal residual disease
Abstract
Purpose: BCR-ABL1–like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a recently identified B-cell ALL (B-ALL)subtype with poor outcome that exhibits a gene expression profile similar to BCR-ABL1-positive ALL but lacks the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein. We examined the outcome of children with BCR-ABL1–like ALL treated with risk-directed therapy based on minimal residual disease (MRD) levels during remission induction.
Patients and methods: Among 422 patients with B-ALL enrolled onto the Total Therapy XV study between 2000 and 2007, 344 had adequate samples for gene expression profiling. Next-generation sequencing and/or analysis of genes known to be altered in B-ALL were performed in patients with BCR-ABL1–likeALL who had available material. Outcome was compared between patients with and those without BCR-ABL1–like ALL.
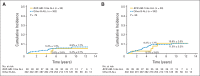
Results: Forty (11.6%) of the 344 patients had BCR-ABL1–like ALL. They were significantly more likely to be male, have Down syndrome, and have higher MRD levels on day 19 and at the end of induction than did other patients with B-ALL. Among 25 patients comprehensively studied for genetic abnormalities, 11 harbored a genomic rearrangement of CRLF2, six had fusion transcripts responsive to ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors or JAK inhibitors, and seven had mutations involving the Ras signaling pathway. There were no significant differences in event-free survival (90.0% +/- 4.7% [SE] v. 88.4% +/- .9% at 5 years; P = .41or in overall survival (92.5% +/- 4.2% v. 95.1% +/- 1.3% at 5 years; P = .41) between patients with and without BCR-ABL1–like ALL.
Conclusion: Patients who have BCR-ABL1–like ALL with poor initial treatment response can be salvaged with MRD-based risk-directed therapy and may benefit from identification of kinase-activating lesions for targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Russell LJ, Capasso M, Vater I, et al. Deregulated expression of cytokine receptor gene, CRLF2, is involved in lymphoid transformation in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009;114:2688–2698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

