Bacillus subtilis Protects Porcine Intestinal Barrier from Deoxynivalenol via Improved Zonula Occludens-1 Expression
- PMID: 25049991
- PMCID: PMC4093535
- DOI: 10.5713/ajas.2013.13744
Bacillus subtilis Protects Porcine Intestinal Barrier from Deoxynivalenol via Improved Zonula Occludens-1 Expression
Abstract
Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) forming the barrier for the first-line of protection are interconnected by tight junction (TJ) proteins. TJ alteration results in impaired barrier function, which causes potentially excessive inflammation leading to intestinal disorders. It has been suggested that toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 ligands and some bacteria enhance epithelial barrier function in humans and mice. However, no such study has yet to be claimed in swine. The aim of the present study was to examine whether Bacillus subtilis could improve barrier integrity and protection against deoxynivalenol (DON)-induced barrier disruption in porcine intestinal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2). We found that B. subtilis decreased permeability of TJ and improved the expression of zonula occludens (ZO)-1 and occludin during the process of forming TJ. In addition, ZO-1 expression of IPEC-J2 cells treated with B. subtilis was up-regulated against DON-induced damage. In conclusion, B. subtilis may have potential to enhance epithelial barrier function and to prevent the cells from DON-induced barrier dysfunction.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; Deoxynivalenol; Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell Line (IPEC-J2); Tight Junction; Zonula Occludens-1.
Figures
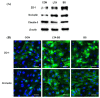
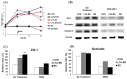

References
-
- Abreu MT. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: How bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:131–144. - PubMed
-
- Aperce CC, Burkey TE, KuKanich B, Crozier-Dodson BA, Dritz SS, Minton JE. Interaction of bacillus species and salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium in immune or inflammatory signaling from swine intestinal epithelial cells. J Anim Sci. 2010;88:1649–1656. - PubMed
-
- Cario E. Barrier-protective function of intestinal epithelial toll-like receptor 2. Mucosal Immunol. 2008;1(Suppl 1):S62–66. - PubMed
-
- Cario E, Gerken G, Podolsky DK. Toll-like receptor 2 enhances zo-1-associated intestinal epithelial barrier integrity via protein kinase C. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:224–238. - PubMed
-
- Cario E, Gerken G, Podolsky DK. Toll-like receptor 2 controls mucosal inflammation by regulating epithelial barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1359–1374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

