(11)C-PIB-PET for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
- PMID: 25052054
- PMCID: PMC6464750
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010386.pub2
(11)C-PIB-PET for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Abstract
Background: According to the latest revised National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke and the Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association (now known as the Alzheimer's Association) (NINCDS-ADRDA) diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer's disease dementia, the confidence in diagnosing mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to Alzheimer's disease dementia is raised with the application of imaging biomarkers. These tests, added to core clinical criteria, might increase the sensitivity or specificity of a testing strategy. However, the accuracy of biomarkers in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias has not yet been systematically evaluated. A formal systematic evaluation of the sensitivity, specificity, and other properties of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with the (11)C-labelled Pittsburgh Compound-B ((11)C-PIB) ligand was performed.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of the (11)C- PIB-PET scan for detecting participants with MCI at baseline who will clinically convert to Alzheimer's disease dementia or other forms of dementia over a period of time.
Search methods: The most recent search for this review was performed on 12 January 2013. We searched MEDLINE (OvidSP), EMBASE (OvidSP), BIOSIS Previews (ISI Web of Knowledge), Web of Science and Conference Proceedings (ISI Web of Knowledge), PsycINFO (OvidSP), and LILACS (BIREME). We also requested a search of the Cochrane Register of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies (managed by the Cochrane Renal Group).No language or date restrictions were applied to the electronic searches and methodological filters were not used so as to maximise sensitivity.
Selection criteria: We selected studies that had prospectively defined cohorts with any accepted definition of MCI with baseline (11)C-PIB-PET scan. In addition, we only selected studies that applied a reference standard for Alzheimer's dementia diagnosis for example NINCDS-ADRDA or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV (DSM-IV) criteria.
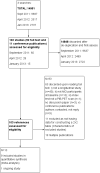
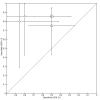
Data collection and analysis: We screened all titles generated by electronic database searches. Two review authors independently assessed the abstracts of all potentially relevant studies. The identified full papers were assessed for eligibility and data were extracted to create two by two tables. Two independent assessors performed quality assessment using the QUADAS 2 tool. We used the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (ROC) model to produce a summary ROC curve.
Main results: Conversion from MCI to Alzheimer's disease dementia was evaluated in nine studies. The quality of the evidence was limited. Of the 274 participants included in the meta-analysis, 112 developed Alzheimer's dementia. Based on the nine included studies, the median proportion converting was 34%. The studies varied markedly in how the PIB scans were done and interpreted.The sensitivities were between 83% and 100% while the specificities were between 46% and 88%. Because of the variation in thresholds and measures of (11)C-PIB amyloid retention, we did not calculate summary sensitivity and specificity. Although subject to considerable uncertainty, to illustrate the potential strengths and weaknesses of (11)C-PIB-PET scans we estimated from the fitted summary ROC curve that the sensitivity was 96% (95% confidence interval (CI) 87 to 99) at the included study median specificity of 58%. This equated to a positive likelihood ratio of 2.3 and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.07. Assuming a typical conversion rate of MCI to Alzheimer's dementia of 34%, for every 100 PIB scans one person with a negative scan would progress and 28 with a positive scan would not actually progress to Alzheimer's dementia.There were limited data for formal investigation of heterogeneity. We performed two sensitivity analyses to assess the influence of type of reference standard and the use of a pre-specified threshold. There was no effect on our findings.
Authors' conclusions: Although the good sensitivity achieved in some included studies is promising for the value of (11)C-PIB-PET, given the heterogeneity in the conduct and interpretation of the test and the lack of defined thresholds for determination of test positivity, we cannot recommend its routine use in clinical practice.(11)C-PIB-PET biomarker is a high cost investigation, therefore it is important to clearly demonstrate its accuracy and standardise the process of the (11)C-PIB diagnostic modality prior to it being widely used.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures




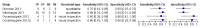


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Forsberg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Forsberg A, Almkvist O, Engler H, Wall A, Langstrom B, Nordberg A. High PIB retention in Alzheimer’s disease in early event with complex relationship with CSF biomarkers and functional parameters. Current Alzheimer Research 2010;7:56‐66. - PubMed
-
- Forsberg A, Engler H, Almkvist O, Blomquist G, Hagman G, Wall A, et al. PET imaging of amyloid deposition in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of Aging 2008;29:1456‐65. - PubMed
-
- Forsberg A, Engler H, Blomquist G, Almkvist O, Hagman G, Wall A, et al. PET imaging of amyloid depositions in MCI patients using PIB. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2007; Vol. 27 Suppl 1:BO03‐01.
Grimmer 2013 {published data only}
-
- GrimmerT, Wutz C, Drzezga A, Forster S, Forstl H, Ortner M, et al. The usefulness of amyloid imaging in predicting the clinical outcome after two years in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Current Alzheimer Research 2013;10:82‐5. - PubMed
Jack 2010 {published data only}
-
- Burns L, Berman R, Guo Z, Soares H, Kaplita S, Yoo B, et al. The relationship between cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers and Pittsburgh compound B (PIB) positron emission tomography (PET) in predicting Alzheimer's disease (AD) [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S206.
-
- Ewers M, Aisen P, Jagust W, Schuff N, Weiner M, Trojanowski J, et al. CSF biomarker and PIB‐PET‐derived beta‐amyloid signature predicts brain metabolism grey matter and cognitive changes in non‐demented subjects [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S102.
-
- Ishii K, Sakata M, Oda K, Toyohara J, Ishiwata K, Senda M, et al. Age, ApoE e4, and ethnic effect on [C‐11] PIB in multinational ADNI studies: Direct comparison of J‐ADNI, US‐ADNI and AIBL data [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S233.
Koivunen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Koivunen J, Karrasch M, Scheinin NM, Aalto S, Vahlberg T, Nagren K, et al. Cognitive decline and amyloid accumulation in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2012; Vol. 34, issue 1:31‐7. - PubMed
-
- Koivunen J, Pirttila T, Kemppainen N, Aalto S, Herukka SK, Jauhianen AM, et al. PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake and cerebrospinal fluid beta‐amyloid in mild cognitive impairment. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008; Vol. 26, issue 4:378‐83. - PubMed
-
- Koivunen J, ScheininN, Virta JR, et al. Amyloid PET imaging in patients with mild cognitive impairment: A 2‐year follow‐up study. Neurology 2011;76:1085‐90. - PubMed
Okello 2009 {published data only}
Ossenkoppele 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ossenkoppele R, Tolboom N, Foster‐Dingley JC, Adriaanse SF, Boellaard R, Yaqub M, et al. Longitudinal imaging of Alzheimer pathology using [11C]PIB, [18F]FDDNP and [18F]FDG PET. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2012;9(6):990‐1000. - PubMed
Ossenkoppele 2012a {published data only}
-
- Ossenkoppele R, Prins ND, Pijnenburg YA, Lemstra AW, Flier WM, Adriaanse SF, et al. Impact of molecular imaging on the diagnostic process in a memory clinic. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2012;9(4):414‐21. - PubMed
Villemagne 2011 {published data only}
-
- Villain N, Chetelat G, Grassiot B, Bourgeat P, Jones G, Ellis KA, et al. Regional dynamics of amyloid‐beta deposition in healthy elderly, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A voxelwise PiB‐PET longitudinal study. Brain 2012; Vol. 135, issue 7:2126‐39. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Choo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Choo H, Lee DY, Seo EH, Kim YK, Yoon EJ, Lee DS, et al. PIB retention changes in cognitively normal, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: One year follow‐up study IL [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S208‐9.
Driscoll 2011 {published data only}
Ellis 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ellis KA, Rowe CC, Villemagne VL, Martins RN, Masters CL, Salvado O, et al. addressing population aging and Al;zheimer's disease through the Australian imaging biomarkers and lifestyle study: collaboration with the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2010;6:291‐6. - PubMed
Fagan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fagan AM, Roe CM, Xiong C, Mintun M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid tau/beta‐amyloid<sub>42</sub> ratio as a prediction of cognitive decline in nondemented older adults. Archives of Neurology 2007; Vol. 64, issue 3:343‐9. - PubMed
Kadir 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kadir A, Alkmvist O, Forsberg A, Wall A, Engler H, Langstrom B at al. Dynamic changes in PET amyloid and FDG imaging at diffetrent stages of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2012;33:198.e1‐198.e14. - PubMed
Kadir 2012a {published data only}
-
- Kadir A, Almkvist O, Forsberg A, Wall A, Engler H, Langstrom B, et al. Dynamic changes in PET amyloid and FDG imaging at different stages of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2012; Vol. 33, issue 1:198.e1‐14. - PubMed
Resnick 2010 {published data only}
Rowe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rowe CC, Ellis KA, Rimajova M, Bourgeat P, Pike KE, Jones G, et al. Amyloid imaging results from the Australian Imaging Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) study of aging. Neurobiology of Aging 2010;31:1275‐83. - PubMed
Shinotoh 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shinotoh H, Shimada H, Hirano S, Tanaka N, Sato K, Kiyoshi F, et al. Longitudinal [11C]PIB PET study in healthy elderly persons, patients with mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S224.
Sojkova 2008 {published data only}
References to ongoing studies
DeKosky 2006 {published data only}
-
- Dekosky ST, Mathis CA, Price JC, Lopresti BJ, Meltzer CC, Ziolko SK, et al. Human amyloid‐imaging studies with Pittsburgh compound‐B in mild cognitive impairment (MCI): Is MCI the critical period of amyloid plaque deposition?. Neurology 2006; Vol. 66, issue 5:A60.
Additional references
Albert 2011
-
- Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging‐Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2011;7(3):270‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Albin 2013
Bacskai 2007
-
- Bacskai BJ, Frosch MP, Freeman SH, Raymond SB, Augustinack JC, Johnson KA, et al. Molecular imaging with Pittsburgh compound B confirmed at autopsy: a case report. Archives of Neurology 2007;64(3):431‐4. - PubMed
Banzo 2014
-
- Banzo I, Jimenez‐Bonilla J, Ortega‐Nava F, Quirce R, Martinez‐Rodriguez I, Arcocha‐Torres M, et al. Amyloid imaging with (11)C‐PIB PET/CT and glucose metabolism with (18)F‐FDG PET/CT in a study on cognitive impairment in the clinical setting. Nuclear Medicine Communications 2014;35(3):238‐44. doi:10.1097/MNM.0000000000000042. - PubMed
Birks 2006
Blennow 2014
Bossuyt 2008
-
- Bossuyt PM, Leeflang MM. Chapter 6: Developing criteria for including studies. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 0.4 2008.
Boxer 2005
-
- Boxer AL, Miller L. Clinical features of frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimer's Disease and Associated Disorders 2005;19 Suppl 1:S3‐6. - PubMed
Brun 1994
Bruscoli 2004
-
- Bruscoli M, Lovestone S. Is MCI really just early dementia? A systematic review of conversion studies. International Psychogeriatrics 2004;16:129‐40. - PubMed
Chen 2014
-
- Chen X, Li M, Wang S, Zhu H, Xiong Y, Liu X. Pittsburgh compound B retention and progression of cognitive status ‐ a meta‐analysis. European Journal of Neurology 2014:doi:10.1111/ene.12398. - PubMed
Cole 2010
Dickson 1992
-
- Dickson DW, Crystal HA, Mattiace LA, Masur DM, Blau AD, Davies P, et al. Identification of normal and pathological aging in prospectively studied nondemented elderly humans. Neurobiology of Aging 1992;13(1):179‐89. - PubMed
Drzezga 2008
-
- Drzezga A. Basic pathologies of neurodegenerative dementias and their relevance for state‐of‐the‐art molecular imaging studies. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2008;35:S4‐11. - PubMed
DSMIII 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd revised edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association 1987.
DSMIV 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association 1994.
Dubois 2010
-
- Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Cummings JL, Dekosky ST, Barberger‐Gateau P, et al. Revising the definition of Alzheimer's disease: a new lexicon. Lancet Neurology 2010;9(11):1118‐27. - PubMed
Ducharme 2013
-
- Ducharme S, Guiot MC, Nikelski J, Chertkow H. Does a positive Pittsburgh compound B scan in a patient with dementia equal Alzheimer disease?. JAMA Neurology 2013;70(7):912‐4. - PubMed
Ellis 2011
-
- Ellis KA, Rowe C, Masters C, Szoeke C, Taddei K, Martins R, et al. Predictors of cognitive decline at 18 month follow up among 1112 participants in the australian imaging, biomarkers and lifestyle flagship study of ageing (AIBL) [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S158.
Engler 2008
-
- Engler H, Santillo AF, Wang SX, Lindau M, Savitcheva I, Nordberg A, et al. In vivo amyloid imaging with PET in frontotemporal dementia. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2008;35(1):100‐6. - PubMed
Espinosa 2013
-
- Espinosa A, Alegret M, Valero S, Vinyes‐Junque G, Hernandez I, Mauleon A, et al. A longitudinal follow‐up of 550 mild cognitive impairment patients: evidence for large conversion to dementia rates and detection of major risk factors involved. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2013;34(3):769‐80.doi:10.3233/JAD‐122002. - PubMed
Forman 2006
Foster 2010
Friedrich 2014
-
- Friedrich MJ. Researchers test strategies to prevent Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2014;311(16):1596‐8. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3891. - PubMed
Geslani 2005
-
- Geslani DM, Tierney MC, Herrmann N, Szalai JP. Mild cognitive impairment: an operational definition and its conversion rate to Alzheimer's disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2005;19(5‐6):383‐9. - PubMed
Gomperts 2012
Gomperts 2013
Hampel 2012
-
- Hampe H, Lista S, Khachaturian ZS. Development of biomarkers to chart all Alzheimer's disease stages: the royal road to cutting the therapeutic Gordian knot. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2012;8(4):312‐36. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.05.2116. - PubMed
Hatashita 2012
-
- Hatashita S, Yamasaki H. PET biomarkers of beta‐amyloid deposition and neuronal injury in mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2012; Vol. 39:S407.
Holland 2012
Jack 2008
Johnson 2007
-
- Johnson KA, Gregas M, Becker JA, Kinnecom C, Moran DH, Smith EK, et al. Imaging of amyloid burden and distribution in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Annals of Neurology 2007;62:229‐34. - PubMed
Johnson 2013
-
- Johnson KA, Minoshima S, Bohnen NI, Donohoe KJ, Foste NL, Herscovitch P, et al. Update on appropriate use criteria for amyloid PET imaging: dementia experts, mild cognitive impairment, and education. Amyloid Imaging Task Force of the Alzheimer's Association and Society for Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013;9(4):e106‐9. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.06.001. - PubMed
Kemppainen 2014
-
- Kemppainen NM, Scheinin NM, Koivunen J, Johansson J, Toivonen JT, Nagren K, et al. Five‐year follow‐up of 11C‐PIB uptake in Alzheimer's disease and MCI. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2014;41(2):283‐9. doi:10.1007/s00259‐013‐2562‐0. - PubMed
Klunk 2004
-
- Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP, et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer's disease with Pittsburgh Compound‐B. Ann Neurol 2004;55(3):306‐19. - PubMed
Knotnerus 2002
Leeflang 2008
-
- Leeflang MM, Moons KG, Reitsma JB, Zwinderman AH. Bias in sensitivity and specificity caused by data‐driven selection of optimal cutoff values: mechanisms, magnitude, and solutions. Clinical Chemistry 2008;54(4):729‐37. - PubMed
Leinonen 2008
-
- Leinonen V, Alafuzoff I, Aalto S, Suotunen T, Savolainen S, Nagren K, et al. Assessment of beta‐amyloid in a frontal cortical brain biopsy specimen and by positron emission tomography with carbon 11‐labeled Pittsburgh compound B. Archives of Neurology 2008;65(10):1304‐9. - PubMed
Maruff 2011
-
- Maruff P, Ellis K, Harrington K, Gale J, Fredrickson A, Darby D, et al. Determining rate of decline in prealzheimer's and Alzheimer's disease AIBL participants using a regular brief cognitive assessment [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S255.
Masliah 2001
-
- Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Sagara Y, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, et al. Beta‐amyloid peptides enhance alpha‐synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America 2001;98(21):12245‐50. - PMC - PubMed
Matthews 2008
-
- Matthews FE, Stephan BC, McKeith IG, Bond J, Brayne C, Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study. Two‐year progression from mild cognitive impairment to dementia: to what extent do different definitions agree?. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2008;56(8):1424‐33. - PubMed
Mattsson 2009
-
- Mattsson N, Zetterberg H, Hansson O, Andreasen N, Parnetti L, Jonsson M, et al. CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. JAMA 2009;302(4):385‐93. - PubMed
McKeith 1996
-
- McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the Consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 1996;47(5):1113‐24. - PubMed
McKeith 2005
-
- McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O'Brien JT, Feldman H, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2005;65:1863‐72. - PubMed
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann GM, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984;34(7):939‐44. - PubMed
McKhann 2011
McShane 2006
Mirra 1991
-
- Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D, Sumi SM, Crain BJ, Brownlee LM, et al. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1991;41(4):479‐86. - PubMed
Mitchell 2009
-
- Mitchell AJ, Shiri‐Feshki M. Rate of progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia‐‐meta‐analysis of 41 robust inception cohort studies. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2009;119(4):252‐65. - PubMed
Morris 1993
-
- Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology 1993;43:2412‐4. - PubMed
Mosconi 2012
-
- Mosconi L, Matthews D, Schmidt M, Andrews R. Characterizing brain amyloid changes using PIB‐PET: Progression, clinical correlates, PIB status and optimized sampling [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2012 Vancouver, BC Canada. Conference Start: 20120714 Conference End: 20120719. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2012.
Neary 1988
-
- Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 1998;51:1546‐54. - PubMed
Newell 1999
-
- Newell KL, Hyman BT, Growdon JH, Hedley‐Whyte ET. Application of the National Institute on Aging (NIA)‐Reagan Institute criteria for the neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 1999;58(11):1147‐55. - PubMed
Oddo 2004
-
- Oddo S, Billings L, Kesslak JP, Cribbs DH, LaFerla FM. Abeta immunotherapy leads to clearance of early, but not late, hyperphosphorylated tau aggregates via the proteasome. Neuron 2004;43(3):321‐32. - PubMed
Okello 2007
-
- Okello A, Edison P, Archer H, Hinz R, Fox N, Kennedy A, et al. Amyloid deposition and cerebral glucose metabolism in mild cognitive impairment: a longitudinal 11c‐PIB and 18f‐FDG PET study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 2007; Vol. 78, issue 2:219‐20.
Perrotin 2011
-
- Perrotin A, Desgranges B, Duval C, Joie R, Mezenge F, Landeau B, et al. The imap project: How does the awareness of memory deficits evolve in the course of Alzheimer's disease? Insights from its relationships to PET b‐amyloid and metabolism measurements [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S742‐3.
Petersen 1999
-
- Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E. Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Archives of Neurology 1999;56:303‐8. - PubMed
Petersen 2004
-
- Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. Journal of Internal Medicine 2004;256:183‐94. - PubMed
Petersen 2009
Price 2005
-
- Price JC, Klunk WE, Loprestil BJ, Lu X, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, et al. Kinetic modelling of amyloid binding in humans using PET imaging and Pittsburgh compound‐B. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2005;25:1528‐47. - PubMed
Quinn 2014
-
- Quinn TJ, Fearon P, Noel‐Storr AH, Young C, McShane R, Stott DJ. Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE) for the diagnosis of dementia within community dwelling populations. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue Issue 4. Art. No.: CD010079. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010079.pub2. - PubMed
Rabinovici 2007
-
- Rabinovici GD, Furst AJ, O'Neil JP, Racine CA, Mormino EC, Baker SL, et al. 11C‐PIB PET imaging in Alzheimer disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurology 2007;68(15):1205‐12. - PubMed
Rabinovici 2011
Rentz 2011
-
- Rentz D, Betensky R, Becker A, England R, Maye J, Gidicsin C, et al. Amyloid deposition in non‐demented elderly predicts longitudinal cognitive decline [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S221.
Rinne 2010
-
- Rinne JO, Brooks DJ, Rossor MN, Fox NC, Bullock R, Klunk WE, et al. 11C‐PiB PET assessment of change in fibrillar amyloid‐beta load in patients with Alzheimer's disease treated with bapineuzumab: a phase 2, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, ascending‐dose study. Lancet Neurology 2010;9(4):363‐72. doi:10.1016/S1474‐4422(10)70043‐0. - PubMed
Roman 1993
-
- Roman GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T, Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH, et al. Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS‐AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 1993;43(2):250‐60. - PubMed
Rowe 2007
-
- Rowe CC, Ng S, Ackermann U, Gong SJ, Pike K, Savage G, et al. Imaging beta‐amyloid burden in aging and dementia. Neurology 2007;68(20):1718‐25. - PubMed
Royall 2014
Rutter 2001
-
- Rutter CA, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta‐analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20:2865‐84. - PubMed
Salloway 2014
SAS Institute 2011
-
- SAS Institute Inc. 2011. SAS/OR® 9.3 User’s Guide: Mathematical Programming. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. SAS/OR® 9.3 User’s Guide: Mathematical Programming Copyright © 2011. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA http://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/ormpug/63975/PDF/default/orm... (access 18 January 2013) .
Savva 2009
-
- Savva GM, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Forster G, Matthews FE, Brayne C, et al. Age, neuropathology, and dementia. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;360(22):230‐9. - PubMed
Schneider 2007
-
- Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Bang W, Bennett DA. Mixed brain pathologies account for most dementia cases in community‐dwelling older persons. Neurology 2007;69(24):2197‐204. doi:01.wnl.0000271090.28148.24 [pii]. - PubMed
Schneider 2009
Serrano‐Pozo 2013
-
- Serrano‐Pozo A, Qian J, Monsell SE, Frosch MP, Betensky RA, Hyman BT. Examination of the clinicopathologic continuum of Alzheimer disease in the autopsy cohort of the National Alzheimer Coordinating Center. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 2013;72(12):1182‐92. doi:10.1097/NEN.0000000000000016. - PMC - PubMed
Shimada 2013
-
- Shimada H, Shinotoh H, Hirano S, Miyoshi M, Sato K, Tanaka N, et al. Beta‐amyloid in Lewy body disease is related to Alzheimer's disease‐like atrophy. Movement Disorders 2013;28(2):169‐75. - PubMed
Shin 2010
-
- Shin J, Lee SY, Kim SJ, Kim SH, Cho SJ, Kim YB. Voxel‐based analysis of Alzheimer's disease PET imaging using a triplet of radiotracers: PIB, FDDNP, and FDG. NeuroImage 2010;52(2):488‐96. - PubMed
Shin 2011
Sperling 2011
-
- Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendation from the National Institute on Ageing‐Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2011;7:1‐10. - PMC - PubMed
Trzepacz 2014
-
- Trzepacz PT, Yu P, Sun J, Schuh K, Case M, Witte MM. Comparison of neuroimaging modalities for the prediction of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's dementia. Neurobiology of Aging 2014;35(1):143‐51. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.06.018. S0197‐4580(13)00279‐0 [pii]. - PubMed
Villain 2011
-
- Villain N, Chetelat G, Grassiot B, Bourgeat P, Jones G, Ellis K, et al. Dynamic of beta‐amyloid deposition in healthy elderly, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A PIB‐PET longitudinal study [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S226‐7.
Villemagne 2008
-
- Villemagne VL, Pike KE, Darby D, Maruff P, Savagee G, Ng S, et al. Aâ deposits in older non‐demented individuals with cognitive decline are indicative of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2008;46:1688‐97. - PubMed
Villemagne 2011a
-
- Villemagne V, Ellis K, Chetelat G, Bourgeat P, Jones G, Martins R, et al. AB accumulation correlates with cognitive decline: Results from the longitudinal aibl study [Conference: Alzheimer's Association International Conference, AAIC 11 Paris France. Conference Start: 20110716 Conference End: 20110721. Conference Publication: (var.pagings)]. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011; Vol. 7, issue 4 Suppl 1:S39.
Visser 2006
-
- Visser PJ, Kester, Jolles J, Verhey F. Ten‐year risk of dementia in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2006;67(7):1201‐7. - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AWS, Westwood ME, Mallet S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155:529‐36. - PubMed
Winblad 2004
-
- Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, et al. Mild cognitive impairment ‐ beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Journal of Internal Medicine 2004;256(3):240‐6. - PubMed
Wolk 2009
World Health Organization 2002
-
- World Health Organization. Mental Health. Alzheimer’s Disease. http:// www.afro.who.int/mentalhealth/related_disease/alyheimer_disease.html. Last updated 18 September 2002 (archives, accessed 4 March 2004).
World Health Organization 2010
-
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD‐10 Version: 2010). http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en (accessed 9 January 2013).
Zhang 2012
-
- Zhang S, Han D, Tan X, Feng J, Guo Y, Ding Y. Diagnostic accuracy of 18 F‐FDG and 11 C‐PIB‐PET for prediction of short‐term conversion to Alzheimer's disease in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2012;66(2):185‐98. doi:10.1111/j.1742‐1241.2011.02845.x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

