Protocol: a simple method for extracting next-generation sequencing quality genomic DNA from recalcitrant plant species
- PMID: 25053969
- PMCID: PMC4105509
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-4811-10-21
Protocol: a simple method for extracting next-generation sequencing quality genomic DNA from recalcitrant plant species
Abstract
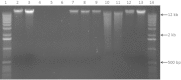
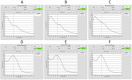
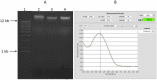
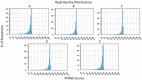
Next-generation sequencing technologies rely on high quality DNA that is suitable for library preparation followed by sequencing. Some plant species store large amounts of phenolics and polysaccharides within their leaf tissue making genomic DNA extraction difficult. While many DNA extraction methods exist that contend with the presence of phenolics and polysaccharides, these methods rely on long incubations, multiple precipitations or commercially available kits to produce high molecular weight and contaminant-free DNA. In this protocol, we describe simple modifications to the established CTAB- based extraction method that allows for reliable isolation of high molecular weight genomic DNA from difficult to isolate plant species Corymbia (a eucalypt) and Coffea (coffee). The simplified protocol does not require multiple clean up steps or commercial based kits, and the isolated DNA passed stringent quality control standards for whole genome sequencing on Illumina HiSeq and TruSeq sequencing platforms.
Keywords: CTAB; Coffea; Corymbia; DNA extraction; Next-generation sequencing.
Figures
References
-
- Thermo Scientific. 260/280 and 260/230 Ratios. T009-Technical Bulletin. 2008. pp. 1–2.
-
- Kasem S, Rice N, Henry RJ. In: Plant Genotyping II: SNP Technology. CAB International, Henry RJ, editor. 2008. DNA Extraction from Plant Tissue; pp. 219–271.
-
- Križman M, Jakše J, Baričevič D, Javornik B, Prošek M. Robust CTAB-activated charcoal protocol for plant DNA extraction. Acta Agric Slov. 2006;87:427–433.
-
- Tibbits JFG, Mcmanus LJ, Spokevicius AV, Bossinger G. A rapid method for tissue collection and high-throughput isolation of genomic DNA from mature trees. Plant Mol Biol Report. 2006;24:81–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02914048. - DOI
-
- Porebski S, Bailey LG, Baum BR. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol Biol Report. 1997;15:8–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02772108. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

