A closer look at rituximab induction on HLA antibody rebound following HLA-incompatible kidney transplantation
- PMID: 25054778
- PMCID: PMC4305036
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2014.261
A closer look at rituximab induction on HLA antibody rebound following HLA-incompatible kidney transplantation
Abstract
Rituximab has been used to increase the efficacy of desensitization protocols for human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-incompatible kidney transplantation; however, controlled comparisons have not been reported. Here we examined 256 post-transplant HLA antibody levels in 25 recipients desensitized with and 25 without rituximab induction, to determine the impact of B-cell depletion. We found significantly less HLA antibody rebound in the rituximab-treated patients (7% of donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) and 33% of non-DSAs) compared with a control cohort desensitized and transplanted without rituximab (32% DSAs and 55% non-DSAs). The magnitude of the increase was significantly larger among patients who did not receive rituximab. Interestingly, in rituximab-treated patients, of the 39 HLA antibodies that increased post transplant, 34 were specific for HLA mismatches present in previous allografts or pregnancies, implying limited efficacy in memory B-cell depletion. Compared with controls, rituximab-treated patients had a significantly greater mean reduction in DSA (-2505 vs. -292 mean fluorescence intensity), but a similar rate of DSA persistence (52% in rituximab treated-and 40% in non-treated recipients). Thus, rituximab induction in HLA-incompatible recipients reduced the incidence and magnitude of HLA antibody rebound, but did not affect DSA elimination, antibody-mediated rejection, or 5-year allograft survival when compared with recipients desensitized and transplanted without rituximab.
Figures
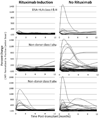
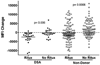
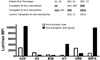
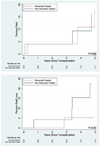
Comment in
-
Does rituximab help in HLA desensitization for kidney transplantation?Kidney Int. 2015 Feb;87(2):277-9. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.365. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 25635721
References
-
- Maloney DG, Liles TM, Czerwinski DK, et al. Phase I clinical trial using escalating single-dose infusion of chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (IDEC-C2B8) in patients with recurrent B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1994;84:2457–2466. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2572–2581. - PubMed
-
- Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, et al. B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:2580–2589. - PubMed
-
- Aranda JM, Jr, Scornik JC, Normann SJ, et al. Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) therapy for acute cardiac humoral rejection: a case report. Transplantation. 2002;73:907–910. - PubMed
-
- Sawada T, Fuchinoue S, Teraoka S. Successful A1-to-O ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation after a preconditioning regimen consisting of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody infusions, splenectomy, and double-filtration plasmapheresis. Transplantation. 2002;74:1207–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

