Effects of emotion regulation difficulties on the tonic and phasic cardiac autonomic response
- PMID: 25054913
- PMCID: PMC4108383
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102971
Effects of emotion regulation difficulties on the tonic and phasic cardiac autonomic response
Abstract
Background: Emotion regulation theory aims to explain the interactions between individuals and the environment. In this context, Emotion Regulation Difficulties (ERD) disrupt the physiological component of emotions through the autonomic nervous system and are involved in several psychopathological states.
Objective: We were interested in comparing the influence of a film-elicited emotion procedure on the autonomic nervous system activity of two groups with different levels of emotion regulation difficulties.
Methods: A total of 63 women (undergraduate students) ranging from 18 to 27 (20.7 ± 1.99) years old were included. Using the upper and lower quartile of a questionnaire assessing the daily difficulties in regulating emotions, two groups, one with low (LERD) and one with high (HERD) levels of emotion regulation difficulties, were constituted and studied during a film-elicited emotion procedure. Cardiac vagal activity (HF-HRV) was analyzed during three periods: baseline, film-elicited emotion, and recovery.
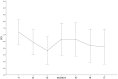
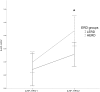
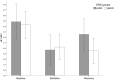
Results: The cardiovascular results showed a decrease in HF-HRV from baseline to elicitation for both groups. Then, from elicitation to recovery, HF-HRV increased for the LERD group, whereas a low HF-HRV level persisted for the HERD group.
Conclusions: The HERD group exhibited inappropriate cardiac vagal recovery after a negative emotion elicitation had ended. Cardiac vagal tone took longer to return to its initial state in the HERD group than in the LERD group. Prolonged cardiac vagal suppression might constitute an early marker of emotion regulation difficulties leading to lower cardiac vagal tone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gross JJ (2007) Handbook of emotion regulation. New York: The Guilford Press. 673 p.
-
- Thompson RA (1994) Emotion Regulation: A Theme in Search of Definition. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development 59: 25–52. - PubMed
-
- Gross JJ, Thompson RA (2007) Emotion regulation: Conceptual foundations. Handbook of emotion regulation. New York, NY US: Guilford Press. 3–24.
-
- Gross JJ (2002) Emotion regulation: Affective, cognitive, and social consequences. Psychophysiology 39: 281–291. - PubMed
-
- Gratz KL, Roemer L (2004) Multidimensional Assessment of Emotion Regulation and Dysregulation: Development, Factor Structure, and Initial Validation of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment 26: 41–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

