Examining the protective role of ErbB2 modulation in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 25055963
- PMCID: PMC4200050
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu150
Examining the protective role of ErbB2 modulation in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
Abstract
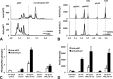
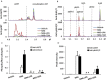
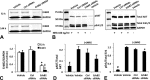
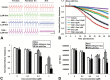
Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are being used as an in vitro model system in cardiac biology and in drug discovery (e.g., cardiotoxicity testing). Qualification of these cells for use in mechanistic investigations will require detailed evaluations of cardiomyocyte signaling pathways and cellular responses. ErbB signaling and the ligand neuregulin play critical roles in survival and functional integrity of cardiac myocytes. As such, we sought to characterize the expression and activity of the ErbB family of receptors. Antibody microarray analysis performed on cell lysates derived from maturing hiPSC-CMs detected expression of ∼570 signaling proteins. EGFR/ErbB1, HER2/ErbB2, and ErbB4, but not ErbB3 receptors, of the epidermal growth factor receptor family were confirmed by Western blot. Activation of ErbB signaling by neuregulin-1β (NRG, a natural ligand for ErbB4) and its modulation by trastuzumab (a monoclonal anti-ErbB2 antibody) and lapatinib (a small molecule ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor) were evaluated through assessing phosphorylation of AKT and Erk1/2, two major downstream kinases of ErbB signaling, using nanofluidic proteomic immunoassay. Downregulation of ErbB2 expression by siRNA silencing attenuated NRG-induced AKT and Erk1/2 phosphorylation. Activation of ErbB signaling with NRG, or inhibition with trastuzumab, alleviated or aggravated doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte damage, respectively, as assessed by a real-time cellular impedance analysis and ATP measurement. Collectively, these results support the expanded use of hiPSC-CMs to examine mechanisms of cardiotoxicity and support the value of using these cells in early assessments of cardiotoxicity or efficacy.
Keywords: ErbB signaling; human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs); nanofluidic proteomic immunoassay (NIA); protein expression; real-time impedance-based cell assay (RTCA) cardio system.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Toxicological Sciences 2014. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modulation of anthracycline-induced myofibrillar disarray in rat ventricular myocytes by neuregulin-1beta and anti-erbB2: potential mechanism for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity.Circulation. 2002 Apr 2;105(13):1551-4. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000013839.41224.1c. Circulation. 2002. PMID: 11927521
-
Mechanisms of cardiotoxicity associated with ErbB2 inhibitors.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Jul;134(2):595-602. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2103-8. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22674190
-
Dehydroevodiamine Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Regulating Neuregulin-1/ErbB Signaling.Cardiovasc Ther. 2024 Dec 7;2024:5538740. doi: 10.1155/cdr/5538740. eCollection 2024. Cardiovasc Ther. 2024. PMID: 39742014 Free PMC article.
-
The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2014 Jan;79:34-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2014. PMID: 24269963 Review.
-
Cardiotoxicity in signal transduction therapeutics: erbB2 antibodies and the heart.Semin Oncol. 2001 Oct;28(5 Suppl 16):18-26. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90278-7. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11706392 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiotoxicity of Antineoplastic Therapies and Applications of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes.Cells. 2021 Oct 21;10(11):2823. doi: 10.3390/cells10112823. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building Multi-Dimensional Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Based Model Platforms to Assess Cardiotoxicity in Cancer Therapies.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 18;12:607364. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.607364. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33679396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concise Review: Precision Matchmaking: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Meet Cardio-Oncology.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Aug;8(8):758-767. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0279. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31020786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Mediating Diabetes-Induced Cardiovascular Complications.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 2;12:701390. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.701390. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34408653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Assessment of Anticancer Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Apr 8;7:50. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00050. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32322588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agarkova I., Perriard J.-C. The M-band: An elastic web that crosslinks thick filaments in the center of the sarcomere. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:477–485. - PubMed
-
- Albini A., Cesana E., Donatelli F., Cammarota R., Bucci E. O., Baravelli M., Anzà C., Noonan D. M. Cardio-oncology in targeting the HER receptor family: The puzzle of different cardiotoxicities of HER2 inhibitors. Future Cardiol. 2011;7:693–704. - PubMed
-
- Aye T. T., Cesana E., Donatelli F., Cammarota R., Bucci E. O., Baravelli M., Anza C., Noonan D. M. Cardio-oncology in targeting the HER receptor family: the puzzle of different cardiotoxicities of HER2 inhibitors. Future Cardiology. 2011;7:693–704. - PubMed
-
- Azim H., Azim H. A., Jr, Escudier B. Trastuzumab versus lapatinib: The cardiac side of the story. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009;35:633–638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

