Targeting human C-type lectin-like molecule-1 (CLL1) with a bispecific antibody for immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 25056598
- PMCID: PMC4280064
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201405353
Targeting human C-type lectin-like molecule-1 (CLL1) with a bispecific antibody for immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
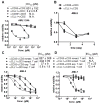
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), which is the most common acute adult leukemia and the second most common pediatric leukemia, still has a poor prognosis. Human C-type lectin-like molecule-1 (CLL1) is a recently identified myeloid lineage restricted cell surface marker, which is overexpressed in over 90% of AML patient myeloid blasts and in leukemic stem cells. Here, we describe the synthesis of a novel bispecific antibody, αCLL1-αCD3, using the genetically encoded unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine. The resulting αCLL1-αCD3 recruits cytotoxic T cells to CLL1 positive cells, and demonstrates potent and selective cytotoxicity against several human AML cell lines and primary AML patient derived cells in vitro. Moreover, αCLL1-αCD3 treatment completely eliminates established tumors in an U937 AML cell line xenograft model. These results validate the clinical potential of CLL1 as an AML-specific antigen for the generation of a novel immunotherapeutic for AML.
Keywords: CLL1; acute myeloid leukemia; bispecific antibodies; cancer immunotherapy; unnatural amino acids.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



References
-
- Gasiorowski RE, Clark GJ, Bradstock K, Hart DNJ. Brit J Haematol. 2014;164:481–495. - PubMed
-
- Walter RB, Appelbaum FR, Estey EH, Bernstein ID. Blood. 2012;119:6198–6208. - PMC - PubMed
- Jin LQ, Hope KJ, Zhai QL, Smadja-Joffe F, Dick JE. Nat Med. 2006;12:1167–1174. - PubMed
- Jin LQ, Lee EM, Ramshaw HS, Busfield SJ, Peoppl AG, Wilkinson L, Guthridge MA, Thomas D, Barry EF, Boyd A, Gearing DP, Vairo G, Lopez AF, Dick JE, Lock RB. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5:31–42. - PubMed
- Kikushige Y, Shima T, Takayanagi S, Urata S, Miyamoto T, Iwasaki H, Takenaka K, Teshima T, Tanaka T, Inagaki Y, Akashi K. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:708–717. - PubMed
- Saito Y, Kitamura H, Hijikata A, Tomizawa-Murasawa M, Tanaka S, Takagi S, Uchida N, Suzuki N, Sone A, Najima Y, Ozawa H, Wake A, Taniguchi S, Shultz LD, Ohara O, Ishikawa F. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:17ra9. - PMC - PubMed
- Majeti R, Chao MP, Alizadeh AA, Pang WW, Jaiswal S, Gibbs KD, Jr, van Rooijen N, Weissman IL. Cell. 2009;138:286–299. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Taussig DC, Pearce DJ, Simpson C, Rohatiner AZ, Lister TA, Kelly G, Luongo JL, Danet-Desnoyers GAH, Bonnet D. Blood. 2005;106:4086–4092. - PMC - PubMed
- van Rhenen A, van Dongen GAMS, Kelder A, Rombouts EJ, Feller N, Moshaver B, Stigtervan Walsum M, Zweegman S, Ossenkoppele GJ, Schuurhuis GJ. Blood. 2007;110:2659–2666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

