Role of SOX family of transcription factors in central nervous system tumors
- PMID: 25057435
- PMCID: PMC4106650
Role of SOX family of transcription factors in central nervous system tumors
Abstract
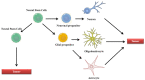
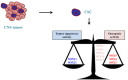
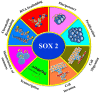
SOX genes are developmental regulators with functions in the instruction of cell fate and maintenance of progenitor's identity during embryogenesis. They play additional roles during tissue homeostasis and regeneration in adults particularly in the Central Nervous System (CNS). In the last years a growing number of evidences has shown that mutations and dysfunction of SOX factors are implicated in several human diseases, including a variety of cancers. In this review, we will summarize the current knowledge about SOX family in CNS tumors and their role in the origin and maintenance of the subpopulation of cancer stem cells in these tumors.
Keywords: CNS tumors; SOX; cell of origin; glioblastoma; glioma stem cell; oncogenic SOX2; therapy target.
Figures
References
-
- Gubbay J, Collignon J, Koopman P, Capel B, Economou A, Munsterberg A, Vivian N, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990;346:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Schepers GE, Teasdale RD, Koopman P. Twenty pairs of sox: extent, homology, and nomenclature of the mouse and human sox transcription factor gene families. Dev Cell. 2002;3:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Bowles J, Schepers G, Koopman P. Phylogeny of the SOX family of developmental transcription factors based on sequence and structural indicators. Dev Biol. 2000;227:239–255. - PubMed
-
- Pevny L, Placzek M. SOX genes and neural progenitor identity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15:7–13. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
