Optic pathway gliomas: a review
- PMID: 25057976
- PMCID: PMC6169473
- DOI: 10.2217/cns.12.47
Optic pathway gliomas: a review
Abstract
Optic pathway gliomas account for 3-5% of all pediatric CNS tumors and represent the most common intrinsic optic nerve tumors. These tumors occur preferentially during the first decade of life and are particularly frequent in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Although optic pathway gliomas are low-grade tumors, their behavior can be aggressive, and their management is often challenging. Their management includes observation, surgery, chemotherapy and radiation. The role of each modality is discussed as well as current and future developments in treatment, in particular targeted therapies that are currently being investigated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

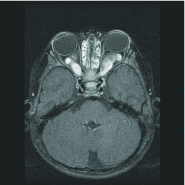
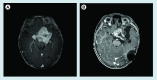
References
-
- Dutton JJ. Gliomas of the anterior visual pathway. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1994;38(5):427–452. - PubMed
-
- Panizza B. [Anatomico-Surgical Remarks on a a Case of Medullary Fungus of the Eye] Pietro Bizzoni, S Bolzani; Pavia, Italia: 1821. pp. 1–45.
-
- Jahraus CD, Tarbell NJ. Optic pathway gliomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2006;46(5):586–596. - PubMed
-
- Michel V. [About hyperplasia of the chiasm and the right optic nerve in the context of elephantiasis] Arch. Ophthalmol. 1873;19:145–164.
▪ Website
-
- www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials/search/view?cdrid=445095&version=HealthPro... National Cancer Institute. Radiation therapy in treating young patients with gliomas.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
