The global burden of disease study 2010: interpretation and implications for the neglected tropical diseases
- PMID: 25058013
- PMCID: PMC4109880
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002865
The global burden of disease study 2010: interpretation and implications for the neglected tropical diseases
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and have the following conflicts: ASB is employed by a commercial company, Inovio Pharmaceuticals. This does not alter our adherence to all PLOS NTDs policies on sharing data and materials. There are no other competing interests to declare.
Figures
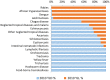


Comment in
-
It's time to dispel the myth of "asymptomatic" schistosomiasis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Feb 19;9(2):e0003504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003504. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 25695740 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, et al. (2012) Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380: 2197–2223. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

