Web-based computational chemistry education with CHARMMing II: Coarse-grained protein folding
- PMID: 25058338
- PMCID: PMC4109841
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003738
Web-based computational chemistry education with CHARMMing II: Coarse-grained protein folding
Abstract
A lesson utilizing a coarse-grained (CG) Gō-like model has been implemented into the CHARMM INterface and Graphics (CHARMMing) web portal (www.charmming.org) to the Chemistry at HARvard Macromolecular Mechanics (CHARMM) molecular simulation package. While widely used to model various biophysical processes, such as protein folding and aggregation, CG models can also serve as an educational tool because they can provide qualitative descriptions of complex biophysical phenomena for a relatively cheap computational cost. As a proof of concept, this lesson demonstrates the construction of a CG model of a small globular protein, its simulation via Langevin dynamics, and the analysis of the resulting data. This lesson makes connections between modern molecular simulation techniques and topics commonly presented in an advanced undergraduate lecture on physical chemistry. It culminates in a straightforward analysis of a short dynamics trajectory of a small fast folding globular protein; we briefly describe the thermodynamic properties that can be calculated from this analysis. The assumptions inherent in the model and the data analysis are laid out in a clear, concise manner, and the techniques used are consistent with those employed by specialists in the field of CG modeling. One of the major tasks in building the Gō-like model is determining the relative strength of the nonbonded interactions between coarse-grained sites. New functionality has been added to CHARMMing to facilitate this process. The implementation of these features into CHARMMing helps automate many of the tedious aspects of constructing a CG Gō model. The CG model builder and its accompanying lesson should be a valuable tool to chemistry students, teachers, and modelers in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

 model (right panel).
model (right panel).
 , as the protein is folded for 62% of the simulation.
, as the protein is folded for 62% of the simulation.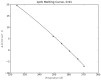
 calculated from a full trajectory.
calculated from a full trajectory.  occurs when
occurs when  , and the curvature of the plot is related to
, and the curvature of the plot is related to  .
.
References
-
- Fersht AR (1999) Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science: A Guide to Enzyme Catalysis and Protein Folding. 2nd edition. New York: Freeman.
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM (2006) Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu Rev Biochem 75: 333–366. - PubMed
-
- Thirumalai D, Klimov D, Dima R (2003) Emerging ideas on the molecular basis of protein and peptide aggregation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13: 146–159. - PubMed
-
- Levitt M, Warshel A (1975) Computer simulation of protein folding. Nature 253: 694–698. - PubMed
-
- Marrink SJ, de Vries AH, Mark AE (2004) Coarse grained model for semiquantitative lipid simulations. J Phys Chem B 108: 750–760.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

