Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action
- PMID: 25058905
- PMCID: PMC4146684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action
Abstract
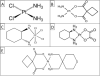
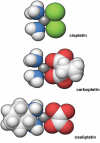
Cisplatin, cisplatinum, or cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II), is a well-known chemotherapeutic drug. It has been used for treatment of numerous human cancers including bladder, head and neck, lung, ovarian, and testicular cancers. It is effective against various types of cancers, including carcinomas, germ cell tumors, lymphomas, and sarcomas. Its mode of action has been linked to its ability to crosslink with the purine bases on the DNA; interfering with DNA repair mechanisms, causing DNA damage, and subsequently inducing apoptosis in cancer cells. However, because of drug resistance and numerous undesirable side effects such as severe kidney problems, allergic reactions, decrease immunity to infections, gastrointestinal disorders, hemorrhage, and hearing loss especially in younger patients, other platinum-containing anti-cancer drugs such as carboplatin, oxaliplatin and others, have also been used. Furthermore, combination therapies of cisplatin with other drugs have been highly considered to overcome drug-resistance and reduce toxicity. This comprehensive review highlights the physicochemical properties of cisplatin and related platinum-based drugs, and discusses its uses (either alone or in combination with other drugs) for the treatment of various human cancers. A special attention is paid to its molecular mechanisms of action, and its undesirable side effects.
Keywords: Cancer treatment; Cisplatin; Mechanisms of action; Platinum-based drugs.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Pryer NK, Cherrington JM. SU11248 inhibits KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta in preclinical models of human small cell lung cancer. Mol.Cancer Ther. 2003;2:471–478. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R, Kaye SB. Ovarian cancer: strategies for overcoming resistance to chemotherapy. Nat.Rev.Cancer. 2003;3:502–516. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal SK. A histochemical approach to the mechanism of action of cisplatin and its analogues. J.Histochem.Cytochem. 1993;41:1053–1073. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal SK, Broomhead JA, Fairlie DP, Whitehouse MW. Platinum drugs: combined anti-lymphoproliferative and nephrotoxicity assay in rats. Cancer Chemother.Pharmacol. 1980;4:249–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

