Met1-linked ubiquitination in immune signalling
- PMID: 25060092
- PMCID: PMC4286102
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.12944
Met1-linked ubiquitination in immune signalling
Abstract
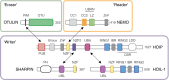
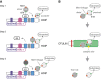
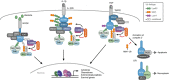
N-terminal methionine-linked ubiquitin (Met1-Ub), or linear ubiquitin, has emerged as a central post-translational modification in innate immune signalling. The molecular machinery that assembles, senses and, more recently, disassembles Met1-Ub has been identified, and technical advances have enabled the identification of physiological substrates for Met1-Ub in response to activation of innate immune receptors. These discoveries have significantly advanced our understanding of how nondegradative ubiquitin modifications control proinflammatory responses mediated by nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases. In this review, we discuss the current data on Met1-Ub function and regulation, and point to some of the questions that still remain unanswered.
Keywords: LUBAC; Met1-linked ubiquitin; NEMO; OTULIN; immune receptor signalling; inflammation; innate immunity.
© 2014 The Authors. FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of FEBS.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

