Comorbidity and functional trajectories from midlife to old age: the Health and Retirement Study
- PMID: 25060316
- PMCID: PMC4336333
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glu113
Comorbidity and functional trajectories from midlife to old age: the Health and Retirement Study
Abstract
Background: The number of diseases and physical functioning difficulties tend to increase with age. The aim of this study was to examine the trajectories of physical functioning across age groups and whether the trajectories differ according to disease status in different population subgroups.
Methods: Repeat data from a nationally representative population sample, the Health and Retirement Study, was used. Participants were 10,709 men and 13,477 women aged 60-107 years at baseline with biennial surveys from 1992 to 2010. Average length of follow-up was 10.3 years ranging from 0 to 18 years. Disease status and physical functioning was asked about at all study phases and 10 items were summed to obtain a physical functioning score (0-10).
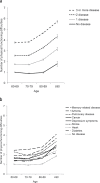
Results: Age modified the relationship between number of chronic diseases and physical functioning with older participants having more physical functioning difficulties with increasing number of diseases. An average 70-year-old participant with no diseases had 0.89 (95% CI: 0.85-0.93) physical functioning difficulties, with one disease 1.72 (95% CI: 1.69-1.76) difficulties, with two diseases 2.57 (95% CI: 2.52-2.62) difficulties, and with three or more diseases 3.82 (95% CI: 3.76-3.88) difficulties. Of the individual diseases memory-related diseases, stroke, pulmonary diseases, and arthritis were associated with significantly higher physical functioning difficulties compared with other diseases.
Conclusions: Comorbidity is associated with greater burden of physical functioning difficulties. Of the studied diseases, memory-related diseases, stroke, pulmonary diseases, and arthritis alone or in combination limit most physical functioning.
Keywords: Aging; Comorbidity; Disability.; Physical functioning.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, Pieper CF, et al. Lower extremity function and subsequent disability: consistency across studies, predictive models, and value of gait speed alone compared with the short physical performance battery. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55:M221–M231. - PubMed
-
- Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49:M85–M94. - PubMed
-
- Deandrea S, Lucenteforte E, Bravi F, Foschi R, La Vecchia C, Negri E. Risk factors for falls in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology. 2010;21:658–668. - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Flood KL. Mobility limitation in the older patient: a clinical review. JAMA. 2013;310:1168–1177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical