A novel approach to formulation factor of aceclofenac eye drops efficiency evaluation based on physicochemical characteristics of in vitro and in vivo permeation
- PMID: 25061410
- PMCID: PMC4099564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2013.03.001
A novel approach to formulation factor of aceclofenac eye drops efficiency evaluation based on physicochemical characteristics of in vitro and in vivo permeation
Abstract
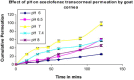
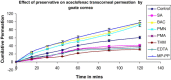
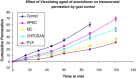
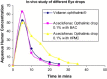
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate aceclofenac eye drop through excised goat cornea. Raising pH of the formulation from 6.0 to 8.0, effect of different preservatives or effect of viscosity enhancer decreases apparent permeability coefficient. Topical ophthalmic NSAID are used to treat ocular surface and anterior segment inflammation as well as post operative management of pain and inflammation. Aceclofenac's unique chemical structure makes it both a potent anti inflammatory drug and lipophilic molecule that penetrates ocular tissue, ensuring relief of pain in cataract and refractive surgery and corneal abrasion. The octanol/water partition coefficient of aceclofenac drug is 1.86 ± 0.75. Permeation characteristics of the drug were evaluated by putting 1 ml formulation on freshly excised goat cornea fixed between donor and receptor compartments of an all-glass modified Franz diffusion cell and measuring the drug permeated in the receptor by spectrophotometry at 275 nm, after 120 min. The results suggest that aceclofenac ophthalmic solution (pH 7) containing BAC provides increased in vitro ocular availability through goat corneas. The combination of methyl paraben and propyl paraben MP-PP preservative in aceclofenac ophthalmic eye drop 0.1% formulated in phosphate buffer increases transcorneal permeation. The developed formulations were evaluated for their pharmacodynamics in albino rabbits, by measuring in-vivo study and were compared to a marketed voltrane ophthalmic solution.
Keywords: Aceclofenac; Cornea; Permeation; Transcorneal.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of in vitro transcorneal approach of aceclofenac eye drops through excised goat, sheep, and buffalo corneas.ScientificWorldJournal. 2015;2015:432376. doi: 10.1155/2015/432376. Epub 2015 Jan 13. ScientificWorldJournal. 2015. PMID: 25654129 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro permeation characteristics of moxifloxacin from oil drops through excised goat, sheep, buffalo and rabbit corneas.Pharmazie. 2007 Nov;62(11):853-7. Pharmazie. 2007. PMID: 18065102
-
Effect of formulation factors on in vitro permeation of moxifloxacin from aqueous drops through excised goat, sheep, and buffalo corneas.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006 Feb 10;7(1):E13. doi: 10.1208/pt070113. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006. PMID: 16584143 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models for Assessing Drug Permeation across the Cornea.Mol Pharm. 2023 Jul 3;20(7):3298-3319. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00195. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37314950 Review.
-
Biopharmaceutical considerations in topical ocular drug delivery.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000 Jul;27(7):558-62. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03288.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10874518 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and ex vivo corneal penetration and absorption models.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016 Dec;6(6):634-647. doi: 10.1007/s13346-015-0275-6. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 26762419 Review.
-
Whole-Eye Perfusion Model for Screening of the Ocular Formulations via Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 Sep 12;20(7):307. doi: 10.1208/s12249-019-1493-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 31515645 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Enteric Coated Elementary Osmotic Tablets of Aceclofenac.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2021 Sep 1;18(4):498-509. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2020.03443. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34496557 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Moxifloxacin Loaded Bilosomes In-Situ Gel: Optimization to Antibacterial Evaluation.Gels. 2022 Jul 4;8(7):418. doi: 10.3390/gels8070418. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35877503 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetry in Drug Permeability through the Cornea.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 11;13(5):694. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050694. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34064834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deepika A., Dhananjay P., Ashim K.M., Indu P.K. Study of the extent of ocular absorption of acetazolamide from a developed niosomal formulation by microdialysis sampling of aqueous humour. Int. J. Pharm. 2007;338:21–26. - PubMed
-
- Faruk O., Emin K., Umit U.I., Selim K., Süleyman S.I., Nursabah E.B., Atila B. Penetration of topical and oral ofloxacin into the aqueous and vitreous humor of inflamed rabbit eyes. Int. J. Pharm. 2000;204:91–95. - PubMed
-
- Ghate D., Edelhauser H.F. Ocular drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006;3:275–287. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh A., Nayak U.K., Roy P. Development, evaluation and method selection for the Preparation of lamivudine microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2007;9:67–71.
-
- Grass G.M., Cooper E.R., Robinson J.R. Mechanisms of corneal drug penetration III: modeling of molecular transport. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006;77:124–126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

