Inactivation of the cardiomyocyte glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) unmasks cardiomyocyte-independent GLP-1R-mediated cardioprotection
- PMID: 25061556
- PMCID: PMC4099509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.04.009
Inactivation of the cardiomyocyte glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) unmasks cardiomyocyte-independent GLP-1R-mediated cardioprotection
Abstract
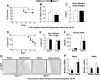
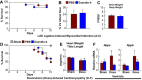
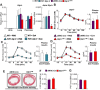
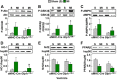
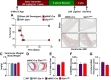
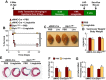
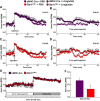
GLP-1R agonists improve outcomes in ischemic heart disease. Here we studied GLP-1R-dependent adaptive and cardioprotective responses to ventricular injury. Glp1r (-/-) hearts exhibited chamber-specific differences in gene expression, but normal mortality and left ventricular (LV) remodeling after myocardial infarction (MI) or experimental doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Selective disruption of the cardiomyocyte GLP-1R in Glp1r (CM-/-) mice produced no differences in survival or LV remodeling following LAD coronary artery occlusion. Unexpectedly, the GLP-1R agonist liraglutide still produced robust cardioprotection and increased survival in Glp1r (CM-/-) mice following LAD coronary artery occlusion. Although liraglutide increased heart rate (HR) in Glp1r (CM-/-) mice, basal HR was significantly lower in Glp1r (CM-/-) mice. Hence, endogenous cardiomyocyte GLP-1R activity is not required for adaptive responses to ischemic or cardiomyopathic injury, and is dispensable for GLP-1R agonist-induced cardioprotection or enhanced chronotropic activity. However the cardiomyocyte GLP-1R is essential for the control of HR in mice.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; Glucagon-like peptide-1; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; HR, heart rate; Heart failure; Incretin; Ischemia; LAD, left anterior descending; MI, myocardial infarction; Myocardial infarction; tGLP-1, truncated forms of GLP-1 such as GLP-1(9–36) or GLP-1(28–36).
Figures
References
-
- Lindenfeld J., Masoudi F.A. Fluid retention with thiazolidinediones: does the mechanism influence the outcome? Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2007;49(16):1705–1707. - PubMed
-
- Scirica B.M., Bhatt D.L., Braunwald E., Steg P.G., Davidson J., Hirshberg B. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine. 2013;369(14):1317–1326. - PubMed
-
- Nikolaidis L.A., Mankad S., Sokos G.G., Miske G., Shah A., Elahi D. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with acute myocardial infarction and left ventricular dysfunction after successful reperfusion. Circulation. 2004;109(8):962–965. - PubMed
-
- Woo J.S., Kim W., Ha S.J., Kim J.B., Kim S.J., Kim W.S. Cardioprotective effects of exenatide in patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: results of exenatide myocardial protection in revascularization study. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2013;33(9):2252–2260. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

