The role of PfEMP1 adhesion domain classification in Plasmodium falciparum pathogenesis research
- PMID: 25064606
- PMCID: PMC4159067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2014.07.006
The role of PfEMP1 adhesion domain classification in Plasmodium falciparum pathogenesis research
Abstract
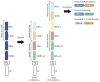
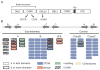
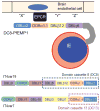
The Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) family has a key role in parasite survival, transmission, and virulence. PfEMP1 are exported to the erythrocyte membrane and mediate binding of infected erythrocytes to the endothelial lining of blood vessels. This process aids parasite survival by avoiding spleen-dependent killing mechanisms, but it is associated with adhesion-based disease complications. Switching between PfEMP1 proteins enables parasites to evade host immunity and modifies parasite tropism for different microvascular beds. The PfEMP1 protein family is one of the most diverse adhesion modules in nature. This review covers PfEMP1 adhesion domain classification and the significant role it is playing in deciphering and deconvoluting P. falciparum cytoadhesion and disease.
Keywords: Antigenic variation; Malaria; Pathogenesis; Plasmodium falciparum; Var.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

