Clinical and functional outcomes after 2 years in the early detection and intervention for the prevention of psychosis multisite effectiveness trial
- PMID: 25065017
- PMCID: PMC4266296
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbu108
Clinical and functional outcomes after 2 years in the early detection and intervention for the prevention of psychosis multisite effectiveness trial
Erratum in
-
Re: McFarlane, W. R., et al: clinical and functional outcomes after 2 years in the early detection and intervention for the prevention of psychosis multisite effectiveness trial. Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):30–43.Schizophr Bull. 2015 Mar;41(2):532. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu219. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25694500 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To test effectiveness of the Early Detection, Intervention, and Prevention of Psychosis Program in preventing the onset of severe psychosis and improving functioning in a national sample of at-risk youth.
Methods: In a risk-based allocation study design, 337 youth (age 12-25) at risk of psychosis were assigned to treatment groups based on severity of positive symptoms. Those at clinically higher risk (CHR) or having an early first episode of psychosis (EFEP) were assigned to receive Family-aided Assertive Community Treatment (FACT); those at clinically lower risk (CLR) were assigned to receive community care. Between-groups differences on outcome variables were adjusted statistically according to regression-discontinuity procedures and evaluated using the Global Test Procedure that combined all symptom and functional measures.
Results: A total of 337 young people (mean age: 16.6) were assigned to the treatment group (CHR + EFEP, n = 250) or comparison group (CLR, n = 87). On the primary variable, positive symptoms, after 2 years FACT, were superior to community care (2 df, p < .0001) for both CHR (p = .0034) and EFEP (p < .0001) subgroups. Rates of conversion (6.3% CHR vs 2.3% CLR) and first negative event (25% CHR vs 22% CLR) were low but did not differ. FACT was superior in the Global Test (p = .0007; p = .024 for CHR and p = .0002 for EFEP, vs CLR) and in improvement in participation in work and school (p = .025).
Conclusion: FACT is effective in improving positive, negative, disorganized and general symptoms, Global Assessment of Functioning, work and school participation and global outcome in youth at risk for, or experiencing very early, psychosis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00531518.
Keywords: assertive community treatment; family psychoeducation; multifamily group; schizophrenia; supported education; supported employment.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Figures
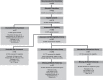

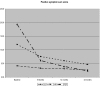




Comment in
-
Psychosocial treatments for clinical high risk individuals.Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):22. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu140. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25316912 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Methodological comments: McFarlane et al.Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):20-1. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu139. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25323580 Free PMC article.
-
Implications for services and policy.Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):25. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu144. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25326636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Early psychosis intervention services: a work in progress.Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):23-4. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu143. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25332408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
More treatment for those most in need? A foregone conclusion?Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):26-7. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu149. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25344948 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Early intervention: how early and with what?Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):4-5. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu160. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 25399025 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Thase M, Comptom M. Evolving treatment strategies in major mental illnesses: focus on schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Medscape Psychiatry & Mental Health. 2008. http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/570240 Accessed August 25, 2011.
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- Wu EQ. The economic burden of schizophrenia in the United States. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66:1122–1129. - PubMed
-
- O’Connell ME, Boat T, Warner KE.eds. Preventing Mental, Emotional and Behavioral Disorders Among Young People. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

